Introduction
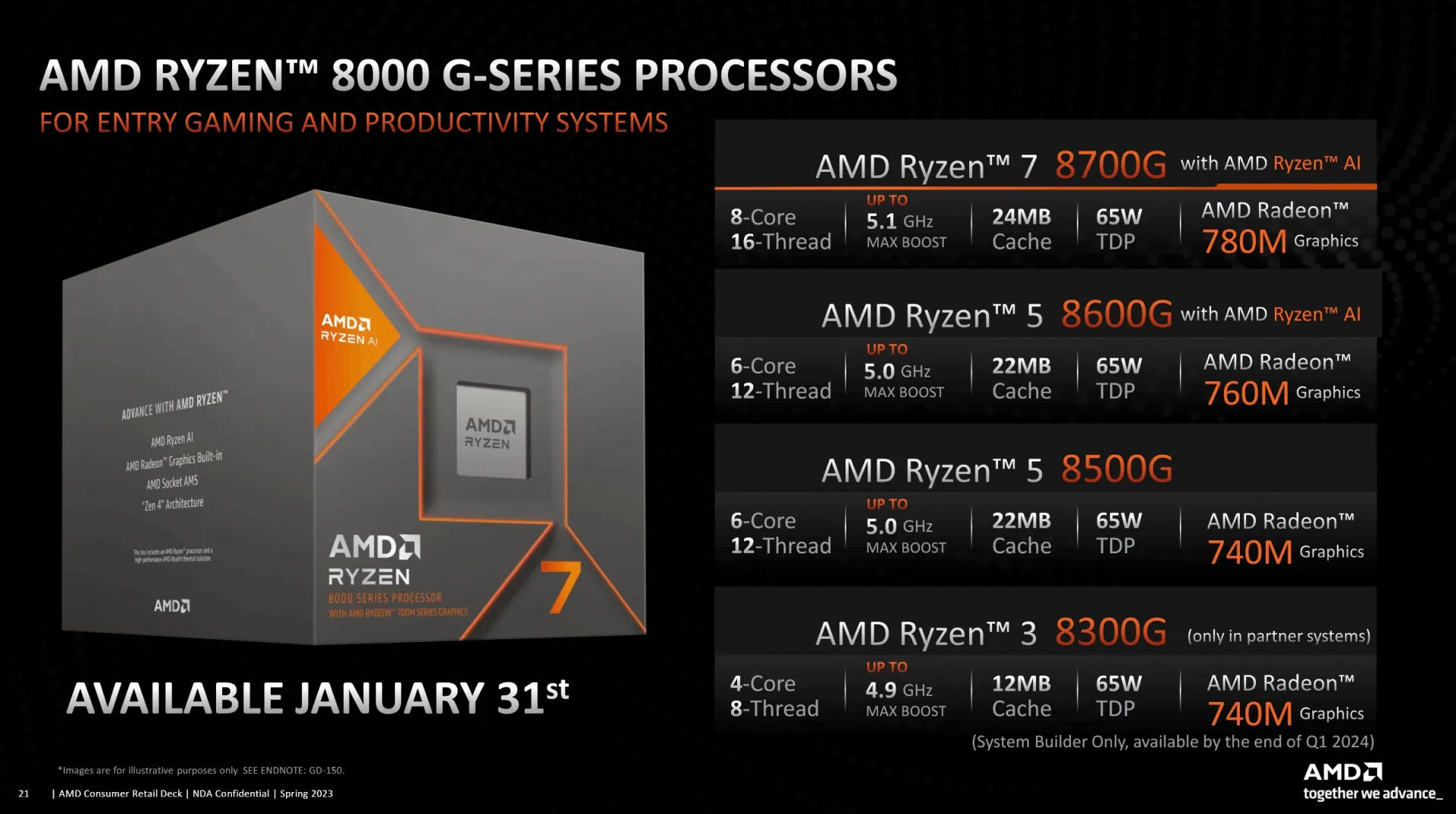
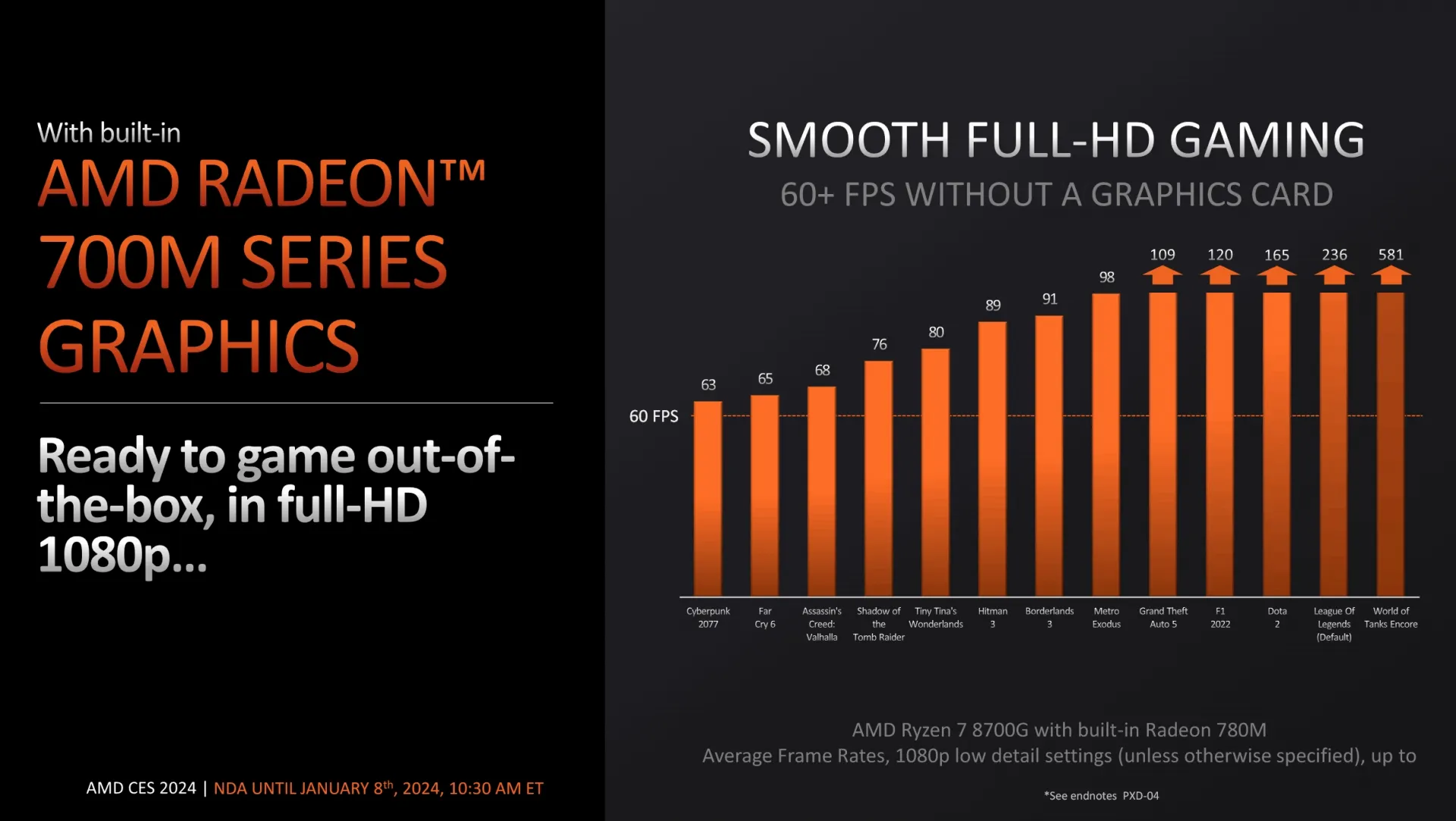
AMD has unveiled its new Ryzen 8000G desktop APU series, marking an update to its existing Ryzen APU lineup. Notably, this release represents the introduction of the first 8000 series for the AM5 socket. Despite the name, these processors are essentially Zen4/RDNA3 mobile chips repurposed for desktop usage. Within the 8000G series, AMD has incorporated its latest CPU and GPU architectures, merging Zen4/Zen4c and RDNA3 graphics capabilities. One standout feature of this series is the inclusion of the XDNA1 Ryzen AI accelerator in select models, such as the 8-core Ryzen 7 8700G and 6-core Ryzen 5 8600G. These models boast a larger silicon footprint. On the other hand, the 6-core 8500G and 4-core 8300G utilize a smaller Phoenix die and do not come equipped with the Ryzen AI processor. The 8300G, featuring Zen4c cores, is exclusively available through OEMs and system integrators. Each SKU within this series maintains a default TDP of 65W and features integrated RDNA3 graphics, available in variations like Radeon 780M (12CU), Radeon 760M (8CU), or Radeon 740M (4CU).
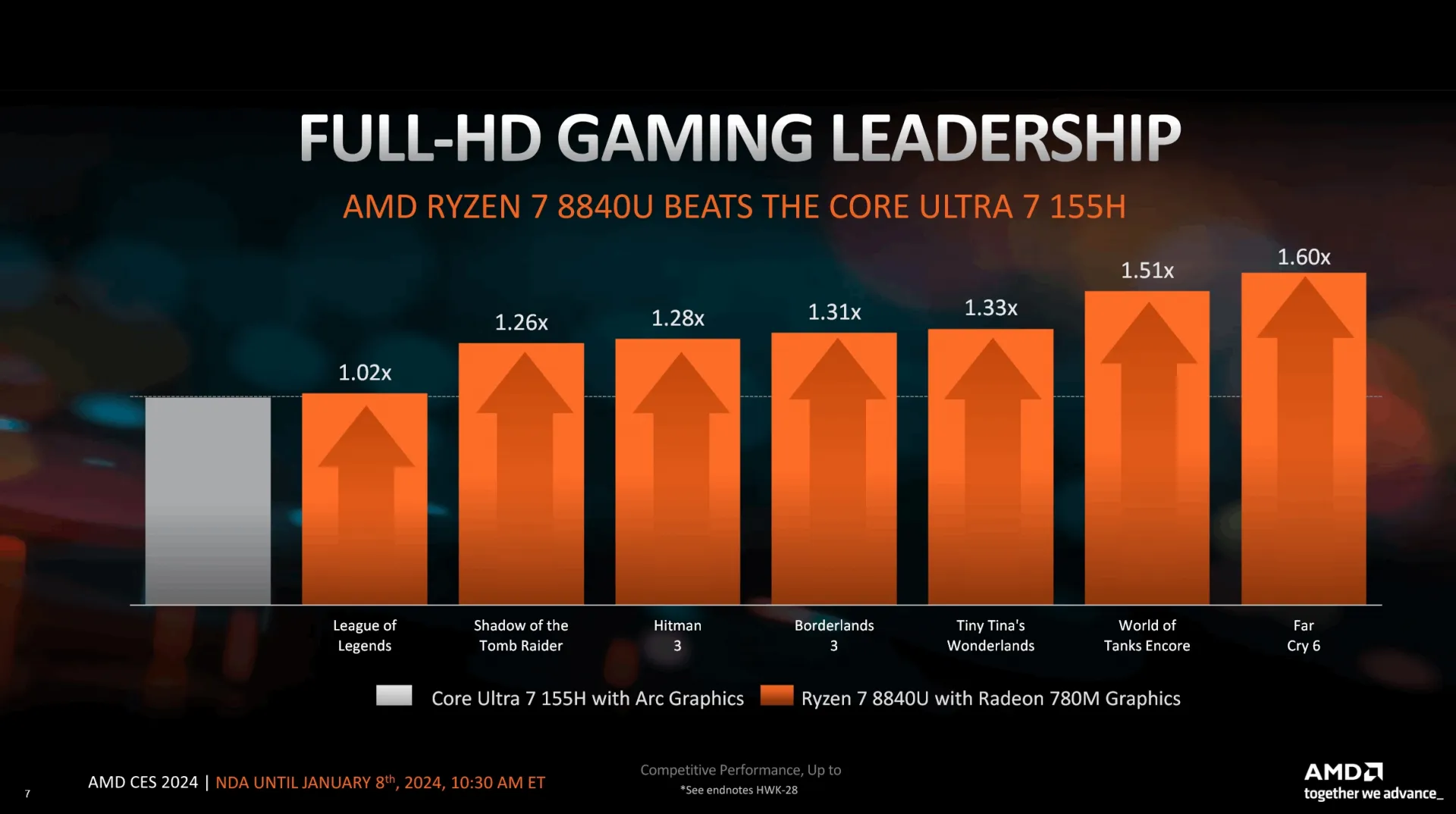
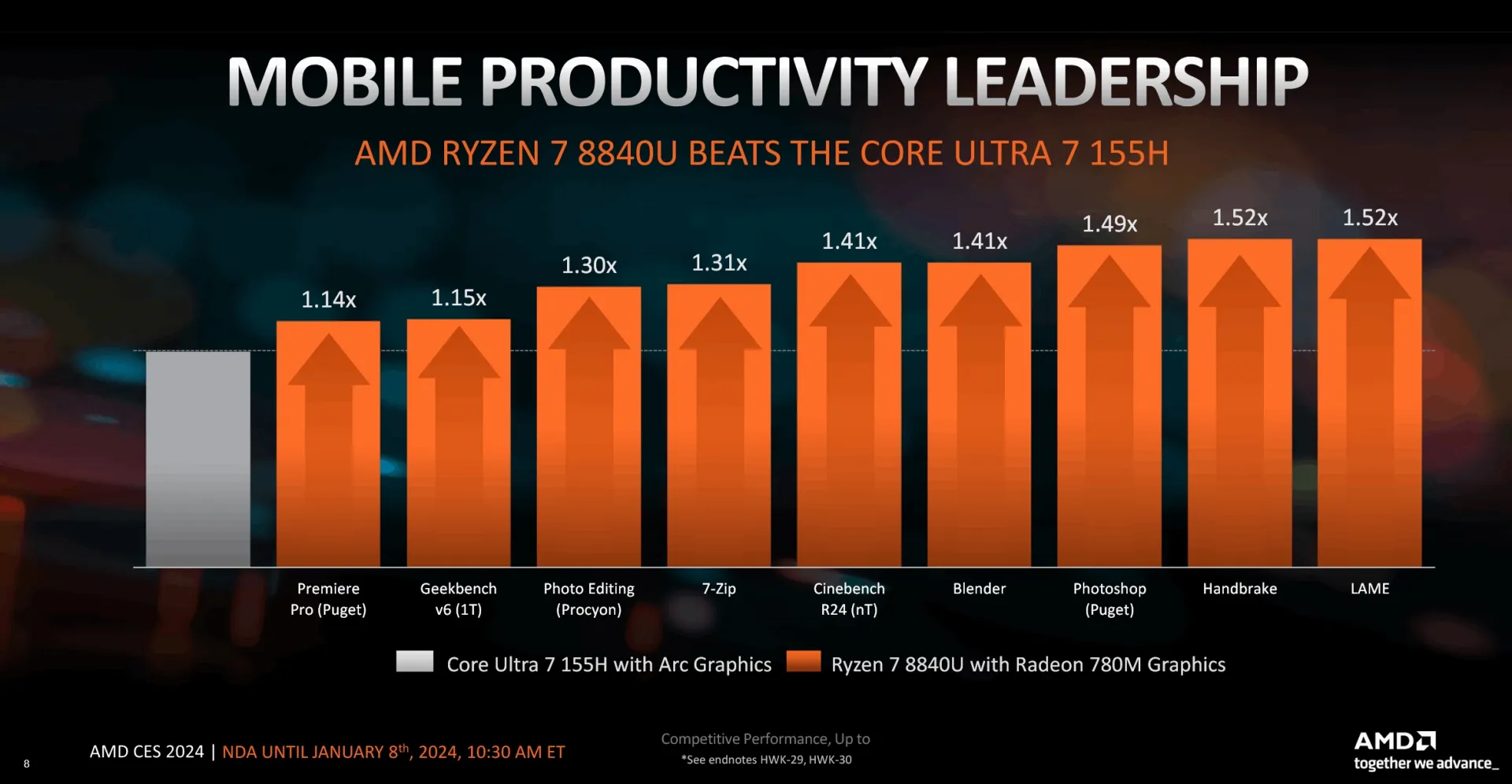
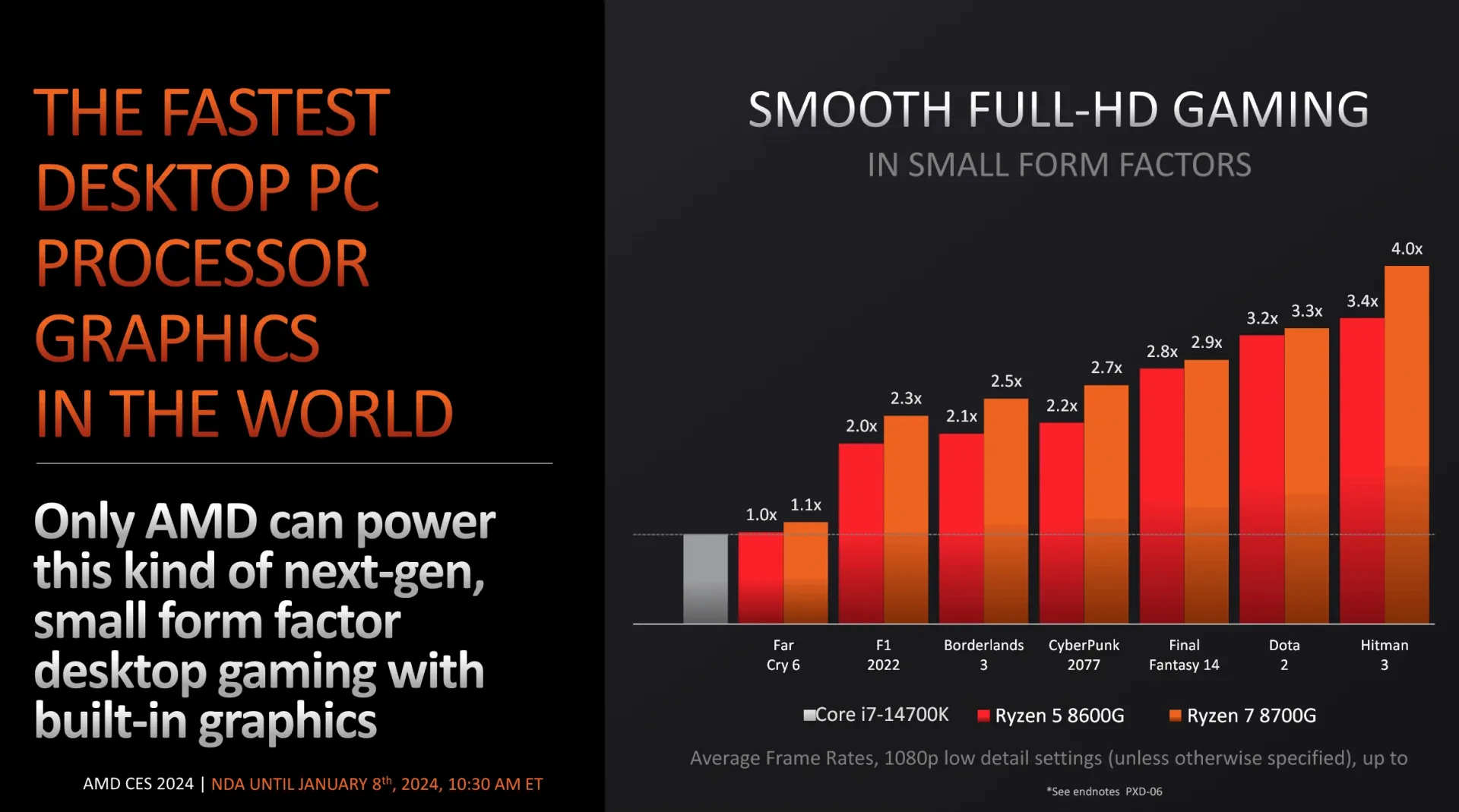
AMD compares the 8700G and 8600G models to Intel’s Core i7-14700K with its integrated UHD Graphics 770, based on the Xe-LP architecture. This comparison is notable as Intel has not released a desktop series with Alchemist integrated graphics. Performance estimates suggest the Ryzen 8600G may outperform the i7-14700K by 1.0 to 3.4 times in low-detail 1080p gaming, with the 8700G potentially achieving 1.1 to 4.0 times higher performance.
In reality, AMD has revised its notebook processor approach for the AM5 socket by offering a similar architecture with adjusted clock speeds and a higher Thermal Design Power (TDP). These processors are now packaged in AM5 instead of Ball Grid Array (BGA) format. This update marks a development for the AM5 socket, expanding its range from eleven to fifteen processors. Notably, this includes the first processors in the series with an integrated Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) capable of supporting gaming applications. Previously, the Ryzen 7000 series was limited to a 2 Compute Unit (CU) RDNA 2 integrated GPU, mainly used for rendering 2D content in Windows environments, with limited gaming capabilities. The desktop variants of these processors, named Phoenix, exhibit a similar segmentation as their notebook counterparts. There are two variants: the first set comprises pure Zen 4 architecture, while the other includes a combination of Zen 4 and Zen 4c cores. AMD's recent announcement specified the clock speeds for the Zen 4 cores. Additionally, AMD has committed to revealing the clock speeds for the less powerful Zen 4c cores soon. AMD consistently uses the term "PXD" or "Phoenix Desktop" when referring to their new APUs in the footnotes of their pre-release press materials. Simultaneously, AMD specifies that the NPU clock speed for the Ryzen 8000G can reach up to 1.6 GHz, which matches the performance of the top-tier solutions in the notebook category, known as Ryzen 8x40 Mobile or "Hawk Point." Additionally, both Phoenix Desktop and Hawk Point share the same TOPS, capped at a maximum of 39 TOPS. Essentially, Phoenix Desktop is equivalent to Hawk Point in terms of specifications. The Ryzen AI feature will only be available in the two larger APUs designed for desktop use, while the two solutions with combined Zen 4-Zen 4c cores do not include this NPU in their hardware.
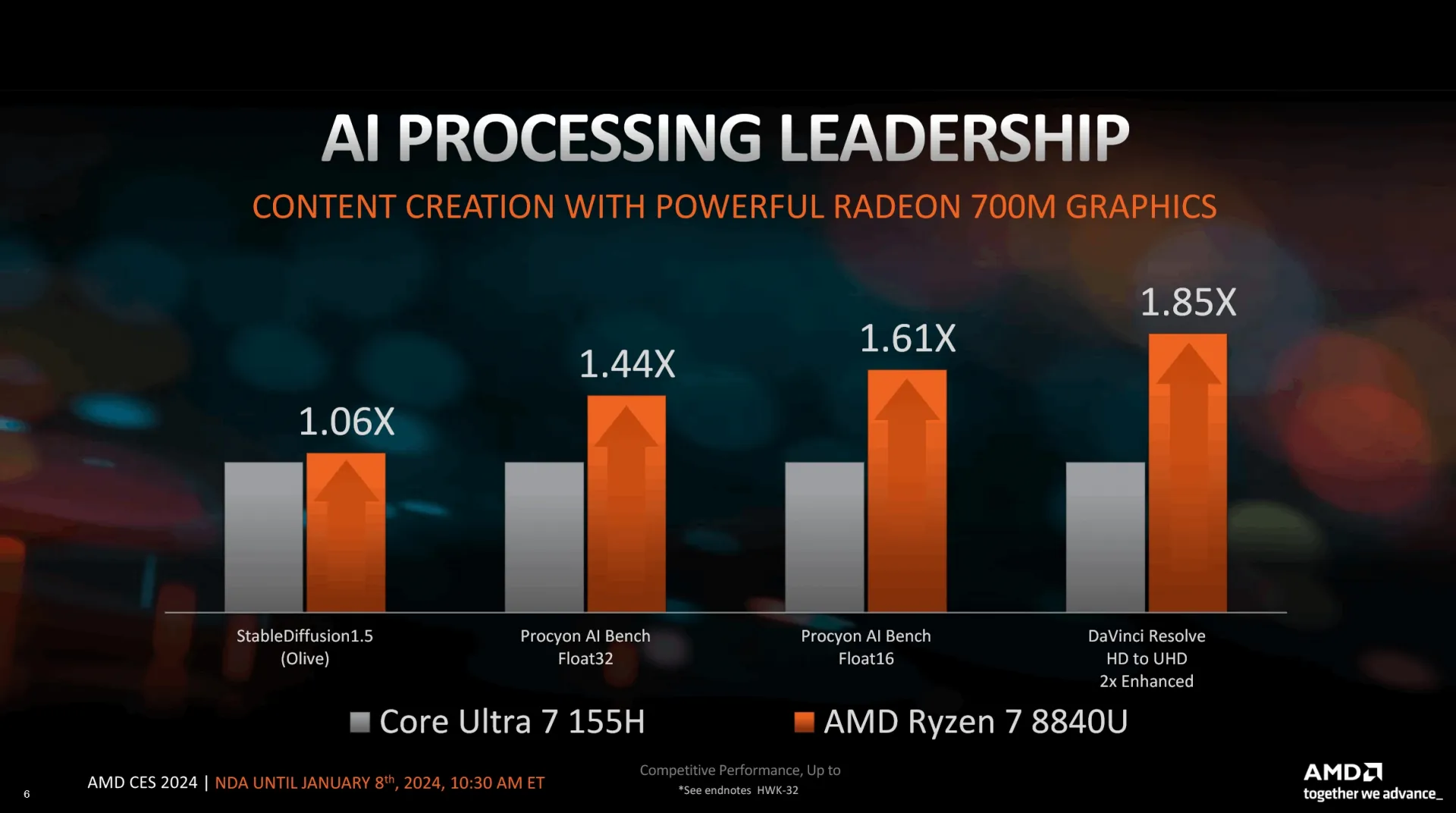
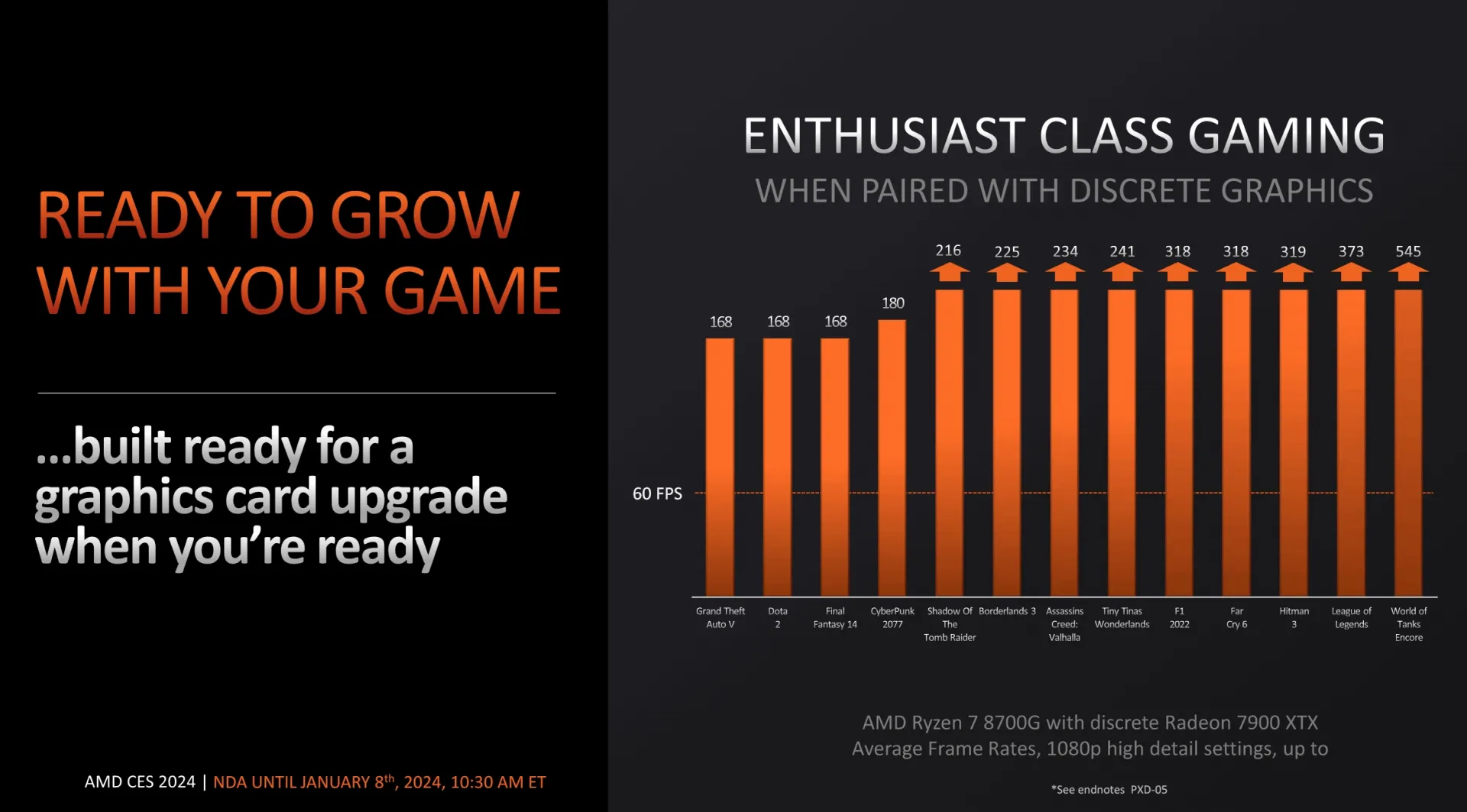
In a comparison involving the 8700G APU and a system comprising a Core i5-13400F and GeForce GTX 1650 desktop graphics card, AMD projects that their integrated solution could deliver gaming performance ranging from 0.89 to 1.31 times that of the Intel/NVIDIA system, with productivity benchmarks showing a 1.1 to 4.6 times improvement. AMD highlights the advantage of not requiring discrete graphics and lower power consumption, with precise figures to be revealed in upcoming reviews.
The Ryzen 8000G series, referred to as 'Hawk Point', encompasses various configurations, detailed as follows:
- Ryzen 7 8700G: 8C/16T, 4.2/5.1 GHz, R780M (12CU) at 2.9 GHz, 65W TDP.
- Ryzen 5 8600G: 6C/12T, 4.35/5.0 GHz, R760M (8CU) at 2.8 GHz, 65W TDP.
- Ryzen 5 8500G: 2C+4c/12T, 3.55/5.0 GHz, R740 (4CU), 65W TDP.
- Ryzen 3 8300G: 1C+3c/8T, 3.45/4.9 GHz, R740 (4CU), 65W TDP.
For comparison, the specifications of the preceding Ryzen 5000G 'Cezanne' and Ryzen 4000G 'Renoir' series are also provided, offering insights into the evolutionary improvements AMD has incorporated in its latest APU series.
|
Model |
Cores/Threads |
Boost / Base Frequency |
Total Cache |
TDP |
NPU |
SEP |
|
AMD Ryzen 7 8700G |
8C/16T |
Up to 5.1GHz / 4.2GHz |
24MB |
65W |
Yes |
$329 |
|
AMD Ryzen 5 8600G |
6C/12T |
Up to 5.0GHz / 4.3GHz |
22MB |
65W |
Yes |
$229 |
|
AMD Ryzen 5 8500G |
6C/12T |
Up to 5.0GHz / 3.5GHz |
22MB |
65W |
N/A |
$179 |
|
AMD Ryzen 3 8300G |
4C/8T |
Up to 4.9GHz / 3.4GHz |
12MB |
65W |
N/A |
N/A |