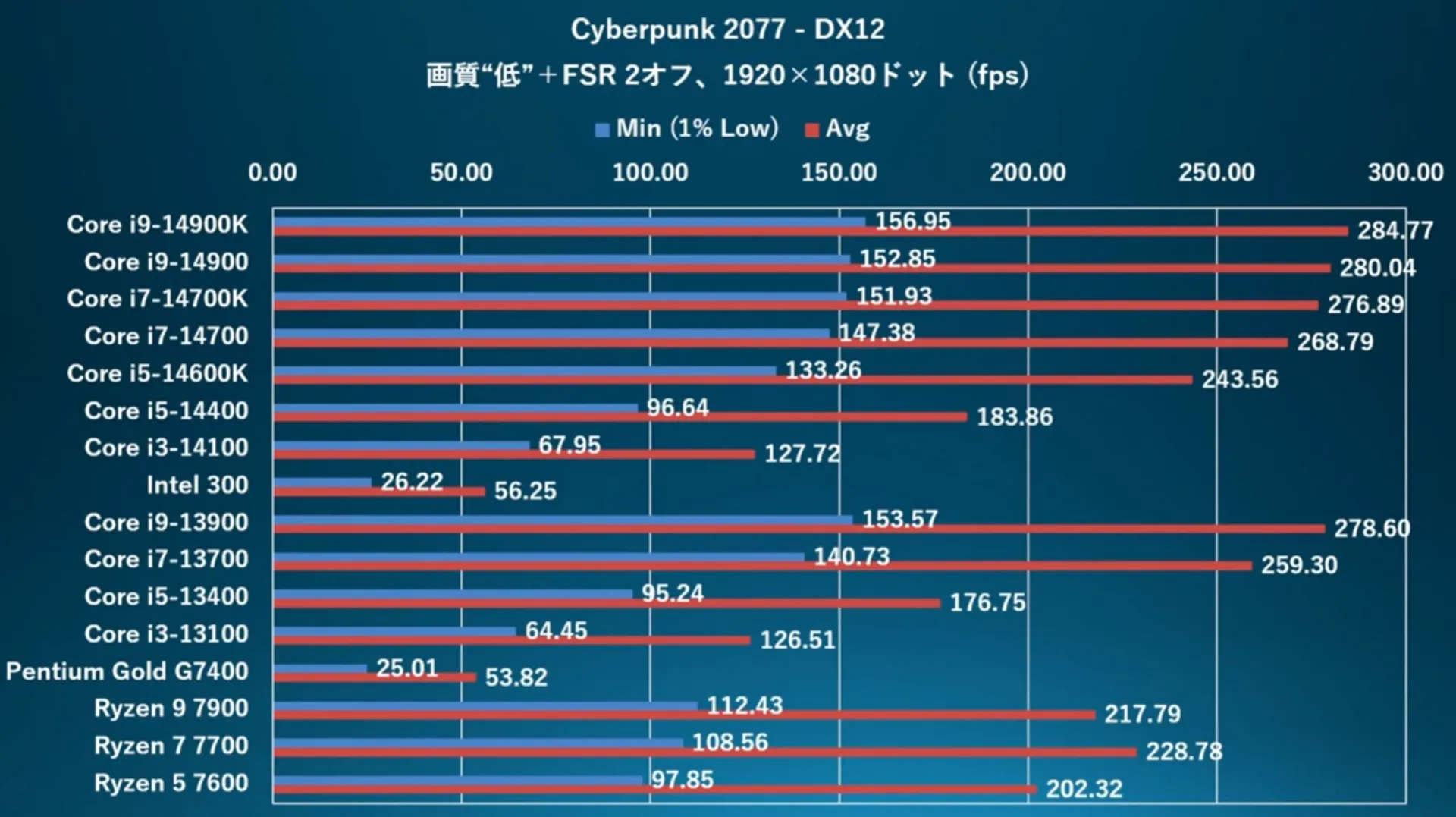
The Intel 300 is part of Intel's Raptor Lake Refresh desktop processors, positioned alongside the more powerful Core i3-14100, a quad-core CPU. When comparing the two, the Core i3-14100 notably outperforms the 300, especially in multi-core performance, with a difference of up to 55% in synthetic benchmarks. This gap is attributed to the i3-14100's higher core count, cache, and frequency.
In gaming benchmarks, the Core i3-14100 emerged as a more effective option, especially for gamers targeting a consistent 60 FPS performance. It consistently maintained a 1% low framerate of at least 60 FPS, ensuring minimal framerate drops. In contrast, the Intel 300 showed significantly lower 1% low framerates in several games, falling below the 60 FPS mark.
The Intel 300's primary advantage lies in its lower power consumption, consuming only 27 watts in certain games like Cyberpunk 2077, compared to the 14100's 65 watts. Additionally, its cost is more affordable, with a suggested retail price between $77 and $87. However, the Core i3-14100 and 14100F, priced at $170 and $125 respectively, offer significantly better performance for a modestly higher cost.
In conclusion, while the Intel 300 CPU marks a continuation of Intel's processor offerings in the dual-core segment, its performance in modern gaming and multitasking scenarios is overshadowed by the more robust Core i3-14100, highlighting the evolving demands of contemporary computing tasks.
Sources: PAD YouTube, VideoCardz, Toms Hardware