Intel processor family
Raptor Lake is Intel's codename for the 13th/14-generation Intel Core CPUs, which will be built on a hybrid architecture with Gracemont power-efficient cores. Raptor Lake, like Alder Lake, will be manufactured utilising Intel's Intel 7 technology. Raptor Lake will have up to 24 cores (8 performance cores + 16 efficiency cores) and 32 threads and will be socket compatible with Alder Lake computers (LGA 1700). Standard features of Raptor Lake desktop CPUs:
- Socket: LGA 1700.
- All the CPUs support up to 128 GB of DDR4-3200 or DDR5-5600 RAM in dual-channel mode.
- All the CPUs support 16x PCI Express Gen 5 and 4x PCI Express Gen 4 lanes, but support may vary depending on motherboard and chipsets.
- Some models feature integrated UHD Graphics 770 GPU with 32 EUs and base frequency of 300 MHz.
- By default, Raptor Lake CPUs are configured to run at Turbo Power at all times and Base Power is only guaranteed when P-Cores/E-cores do not exceed the base clock rate.
- Max Turbo Power: the maximum sustained (> 1 s) power dissipation of the processor as limited by current and/or temperature controls. Instantaneous power may exceed Maximum Turbo Power for short durations (≤ 10 ms). Maximum Turbo Power is configurable by system vendor and can be system specific.
- K model CPUs feature ECC memory support only when paired with a motherboard based on the W680 chipset. Other SKUs do not support ECC memory.
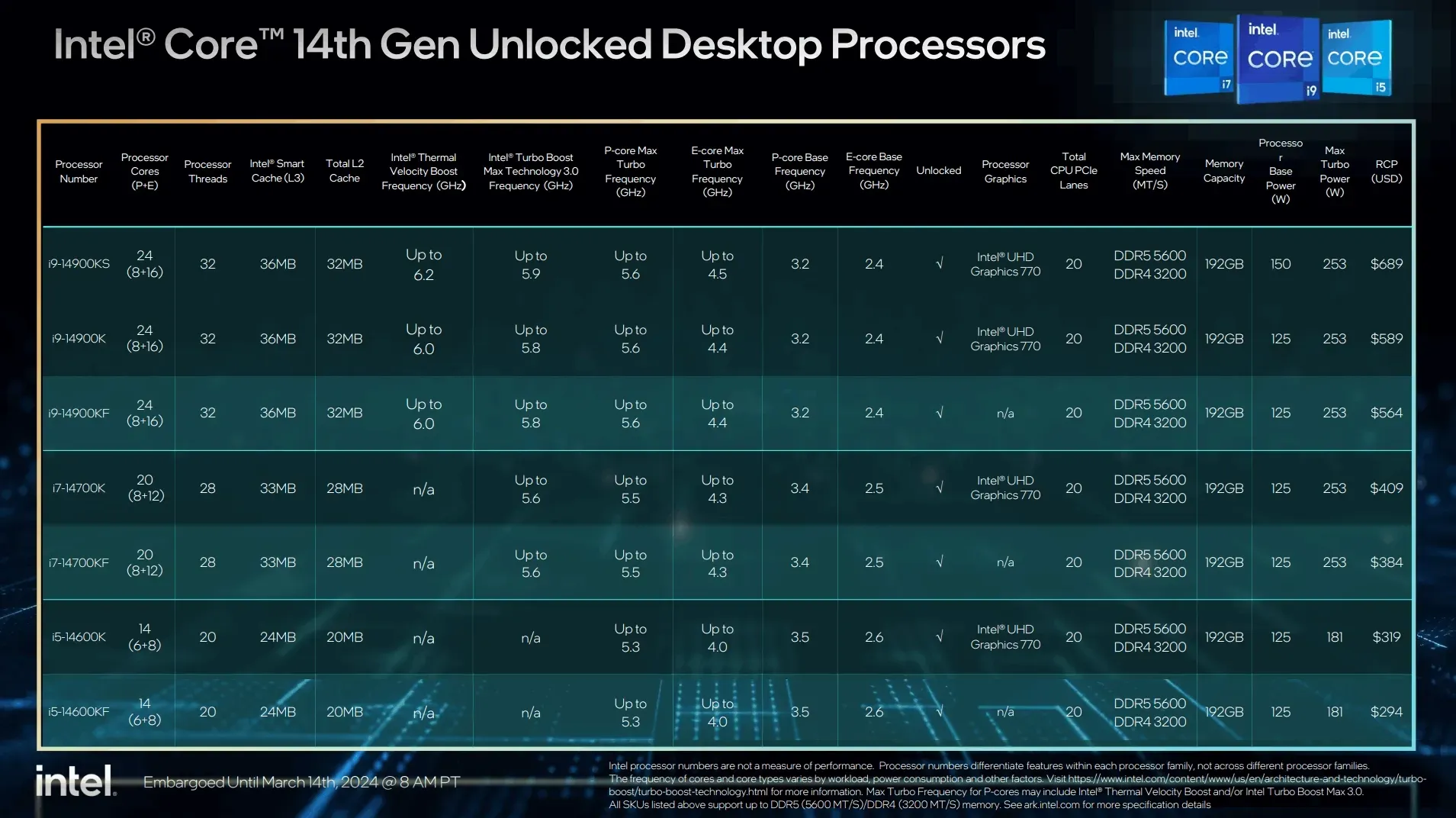
Raptor Lake can be considered an advancement over Alder Lake, using the same node and hybrid architecture. A deeper exploration of this architecture will be discussed subsequently. When assessing the specifications, Intel has shifted its emphasis to higher core counts, increased clock speeds, and enhanced cache sizes, positioning itself competitively against gaming-centric CPUs such as the Ryzen 7 7000 series and Ryzen Series 7000 X3D processors.
Despite the rise in core counts, Intel has chosen not to augment the P-core number, but rather to amplify the E-core quantity, which might be advantageous for intensive multitasking. It's worth noting that E-cores lack Hyperthreading capability. As a reference, the Core i9-14900K is equipped with 24 cores but only yields 32 threads. Additionally, the peak clock rate for the Core i9-14900K reaches 6.0 GHz. A prominent distinction from Alder Lake is Raptor Lake's L2 cache, which is doubled, potentially benefiting cache-dependent gaming experiences. Power limitations are still substantial, consistent with those seen in the 12th-generation CPUs. In this iteration, Intel has slightly elevated the power thresholds, marking a 12W increase for the i9 and i7 models and a 31W escalation for the i5. Considering the 12th-generation CPUs were already thermally challenged, the added power coupled with an augmented core count might not introduce a pronounced impact.
Key advancements of the i9-14900KS include:
- A maximum turbo frequency of 6.2 GHz with Intel Thermal Velocity Boost, marking it as one of the fastest processors in the market.
- A configuration of 24 cores, comprising 8 Performance-cores and 16 Efficient-cores, alongside 32 threads, a 150-watt base power, and a 36MB Intel Smart Cache.
- The processor supports 20 PCIe lanes, with 16 lanes for PCIe 5.0 and 4 lanes for PCIe 4.0, ensuring high-speed connectivity and data transfer capabilities.
- It offers enhanced Intel Application Performance Optimization (APO), contributing to an 11% performance increase in supported gaming titles. The APO feature now supports 14 gaming titles, with plans for further expansion.
- Compatibility with DDR5 5600 MT/s or DDR4 3200 MT/s memory, and support for up to 192GB, catering to high-demand computing tasks.
- The i9-14900KS is compatible with Z790 and Z690 motherboards, with an updated BIOS recommended to optimize gaming and content creation performance.
13th and now 14-generation CPUs have the same Intel 7 manufacturing process and a hybrid design. To improve multitasking performance while minimising power and thermal demands, cores are divided into performance (P) cores and efficient (E) cores. Intel stuck with the same Gracemont E-cores that debuted in Alder Lake, only increasing their number on the chip. However, Intel has verified that the P-cores feature the new Raptor Cove microarchitecture. According to Intel, the revised architecture has "enhanced speed routes." For the refresh generation, frequency climbed, allowing Raptor Lake CPUs to run at greater clock rates than Alder Lake rivals. The new architecture also has 2MB of L2 cache per core, double the amount available on Alder Lake. Intel is adopting a bigger die to fit more E-cores and their cache to accommodate more power. The numerous cores and their varying designs are linked by a broader computing fabric that spans the die. The new fabric enables higher clock rates of up to 1100MHz than the previous generation and adds up to 36MB of shared L2 cache. Intel's bulk of performance gains is still due to frequency and thread count. Along with hardware enhancements, Intel also mentioned it is working to optimise features such as Intel Thread Director, which helps distribute workloads to the most appropriate core.