Page 3
Very blunt: HD = More lines = more pixels = better picture quality
In simple terms the image you will see with HD will have vastly improved image detail and color reproduction.
HDMI means High-Definition Multimedia Interface. It is a new kind of digital audio and video connector that will replace all connectors currently used by DVD players, TV sets and video monitors. The big idea here is that we should all use a single cable instead of several cables when connecting your DVD player to your TV set, for example. Interesting fact... HDMI is similar to DVI with three exceptions... HDMI is a much smaller connector (it pretty much looks like an USB connector), HDMI utilizes copy protection called HDCP (high definition copy protection) and finally; HDMI carries multi channel digital audio. HDMI, like DVI, is ALL-digital therefore picture quality is perfect from source to display.
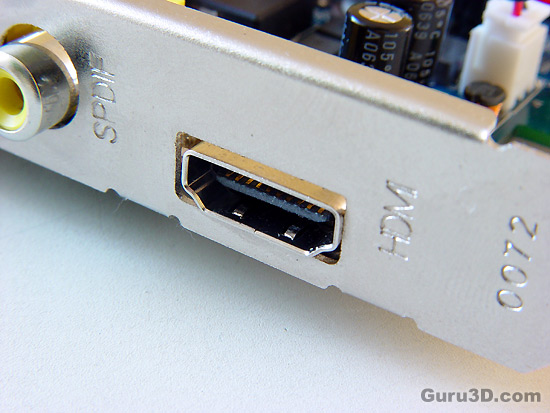

It is possible to connect a device that uses DVI to another that uses HDMI, thru a cable with a HDMI connector at one end and a DVI connector at the other. it is what we have been doing for a while now and was mentioned in several of our articles.
HDMI also implements a copy-protection mechanism called HDCP (High-Bandwidth Digital Copy Protection). First off... from now on, all series 7 cards with HDMI from Galaxy are HDCP compatible as they'll include a crypto chip as default. Why the need for it ? Well... with Vista when you want to playback HDCP content (movies) on your monitor... the resolution could be dumbed down or even worse if your monitor, content and graphics card do not have a HDCP (content protection) handshake. It's like this: your screen will go black during playback, if you do not have a HDCP encoder chip working on the graphics card. So close to the cooler you'll notice a small EEPROM slash CryptoROM doing that magic for you. Galaxy included it on these boards. Mind you that if you like to playback media files with a HDCP ready graphics card... you'll also need a HDCP compatible monitor (hey don't look so angry... don't shoot the messenger!).
So .. a HD Ready television will have either a DVI (Digital Video Interface) or HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface). Both connections provide exceptional quality, HDMI is often referred to as the digital SCART cable as it also provides audio. DVI supplies picture only, separate cables are needed for audio. Both HDMI and DVI support HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection) which will be a requirement for protected content.
 National geographic channel HD broadcast - HDCP content protected.
National geographic channel HD broadcast - HDCP content protected.
Standard and High definition Decoding with PureVideo HD
For this 110 EUR HDMI HDCP ready graphics card there's a neat little trick you can pull with NVIDIA GeForce graphics cards starting at series 7. NVIDIA made the GPU (the graphics chip) an important factor in en/decoding video streams. With a special software suite called PureVideo you can offload the video encoding/decoding process from the CPU towards the GPU, and the best thing yet it can greatly enhance image quality.
PureVideo HD is is a video engine built into the GPU (this is dedicated core logic) and thus is dedicated GPU-based video processing hardware, software drivers and software-based players that accelerate decoding and enhance image quality of high definition video in the following formats: H.264, VC-1, WMV/WMV-HD, and MPEG-2 HD.
So what are the key advantages of PureVideo? In my opinion two key factors are a big advantage. To offload the CPU by allowing the GPU to take over a huge sum of the workload. HDTV decoding through a TS (Transport Stream) file, for example, can be very demanding for a CPU. These media files can peak to 20 Mbit/sec easily as HDTV streams offer high-resolution playback in 1280x720p or even 1920x1080p without framedrops and image quality loss.
By offloading that big task for the bigger part of the graphics core, you give the CPU way more headroom to do other which makes your PC actually run normal. The combination of these factors offer you stutter-free high quality and high resolution media playback. All standard HDTV resolutions of course are supported, among them the obvious 480p, 720p and 1080i modes and now also 1080P (P=Progressive and I=Interlaced). Ever since the Series 75 ForceWare driver, PureVideo is doing something I've been waiting on for quite some time now, 2-2 pull down which converts 24 frames per second to 50 frame per second PAL. But along with this the new G80 series (and this'll work on G70 as well) will offer HD noise reduction, which is great feature with older converted films. And this is where we land at Image Quality. PureVideo can offer a large amount of options that'll increase the IQ of playback. This can be managed with a wide variety of options. Obviously NVIDIA has some interesting filters available in the PureVideo suite like advanced de-interlacing, which can greatly improve image quality while playing back that DVD, MPEG2 or TS file (just some examples). Aside from that, things like color corrections should not be forgotten. All major media streams are supported by NVIDIA with PureVideo. And yes High Definition H.264 acceleration, which will become a big, new and preferred standard, is also supported.
Paradox: You do not need PureVideo for HDTV playback and connectivity, but it is recommended if you have that dedicated hardware in your system anyway.
Once you offload media streams to the graphics processor things look much better with the help of PureVideo. Have a look at the graph below where you are monitoring the CPU at work at roughly 12-20% decoding a HDTV .TS file
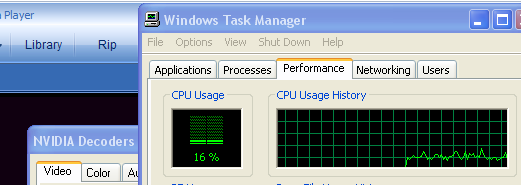
Indeed, a huge improvement over standard decoding. We are now at a CPU utilization of 12-20%, really nice for a HD MPEG2 stream. The processor is almost doing nothing. This for example is a Transport Stream file with a HDTV resolution of 1920x1080i.
In combo with the new drivers you can now also decode High Definition H.264 streams. H.264 is a compression algorithm used to transmit video efficiently between endpoints. This algorithm is seen as the replacement for its predecessor, H.263. What is different about H.264 is that it promises to deliver high quality video, H.264 also enables very high quality encoding, producing way better results than even MPEG2 and of course HDTV levels. These GeForce series 7 and 8 cards can also manage 3:2 and 2:2 pull down (inverse telecine) of SD and HD interlaced content.
New with the introduction of GeForce 8800 we see a 10-Bit display processing pipeline and also new post-processing options (works for GeForce series 7 as well):
- Adds VC-1 & H.264 HD Spatial-Temporal De-Interlacing
- Adds VC-1 & H.264 HD Inverse Telecine
- Adds HD Noise Reduction
- Adds HD Edge enhancement
With the new PureVideo engine the popular benchmark tool HQV now will score 128 points, which is near perfect.
Software like WinDVD, PowerDVD and Nero showtime will support PureVideo from within their software. You can also buy the PureVideo software for a few tenners at NVIDIA after which MediaPlayer or Media Center will work with it flawlessly.
To give you an idea how intensely big one frame of 1920x1080 is with a framerate of 24 frames per second. Click on a the two example images above. Load them up, and realize that your graphics card is displaying that kind of content 24 times per second, while enhancing them in real-time.


