The use of liquid metal for processor cooling is a popular method among some firms and users, as demonstrated by the PlayStation 5. However, it is not suitable for all situations because liquid metal conducts electricity and heat, which can cause damage to equipment if it spreads to certain areas.
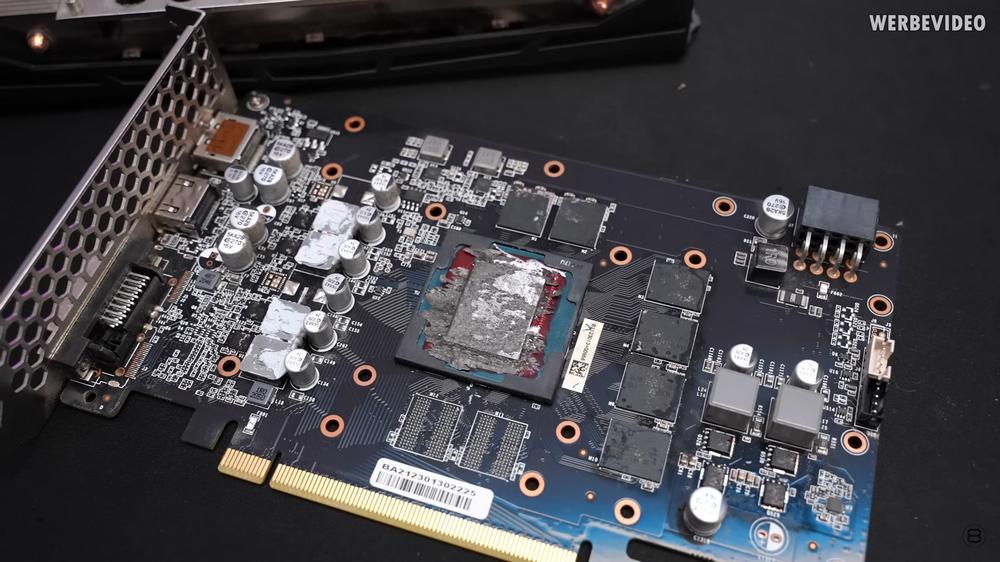
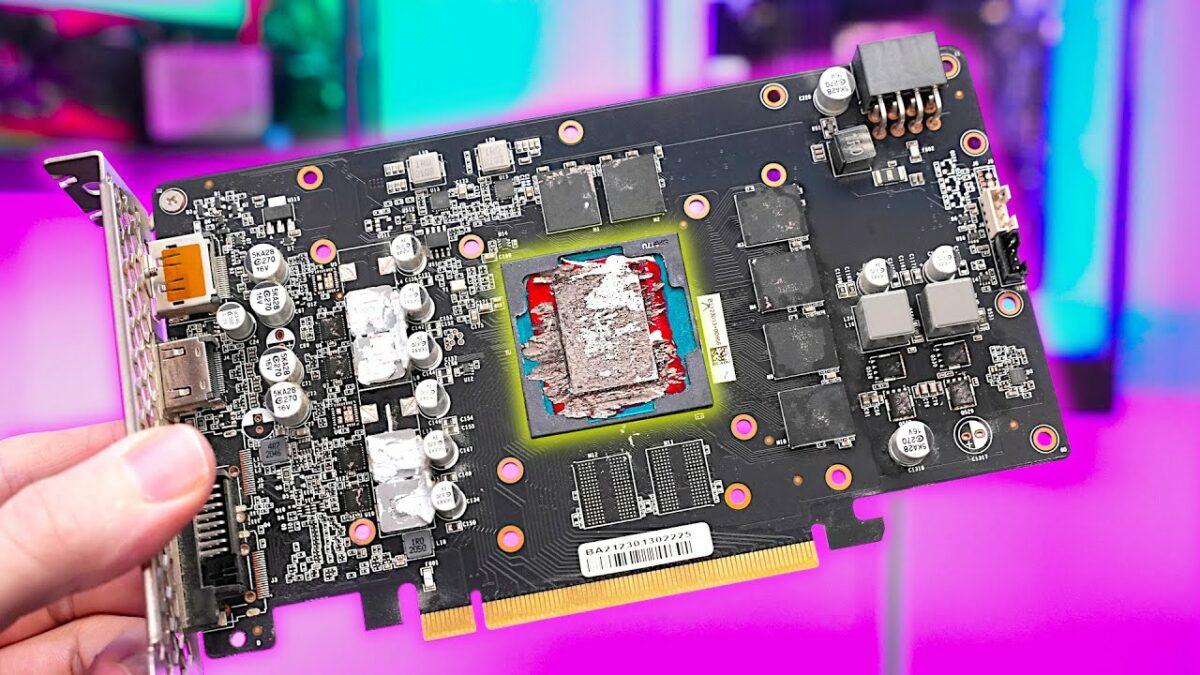
Recently, YouTuber Der8auer received a NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2060 graphics card from a subscriber that had liquid metal applied to it and was experiencing high temperatures above 100 °C (video). Further investigation revealed that the issues were concentrated in the cooling system and there were no other flaws present on the video card.
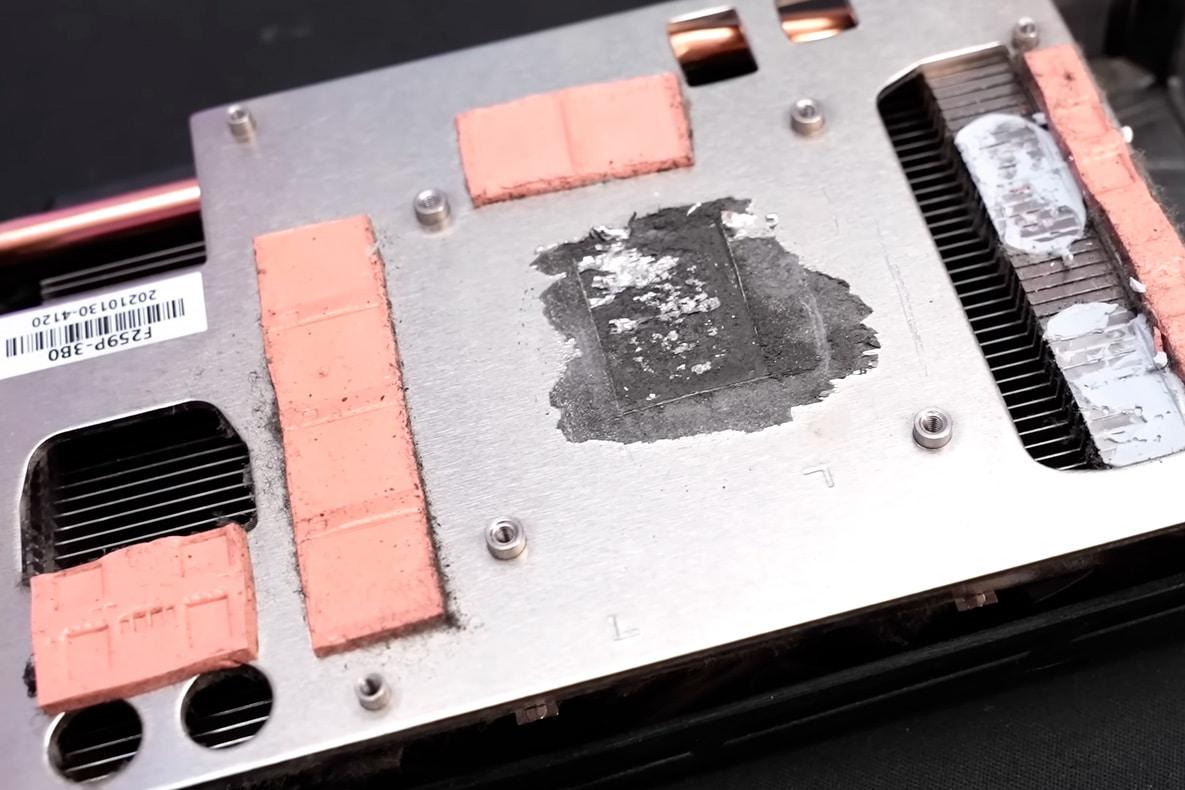
One of the key considerations when using liquid metal is that it should not be used as a thermal paste on aluminum-containing components. This is because liquid metals, such as gallium, can react with aluminum and form an alloy that can make the aluminum brittle and ultimately cause damage to the hardware. In the case presented, the GPU had an aluminum cooler and the liquid metal had formed an alloy that was damaging the equipment.
Despite this, he was able to recover the subscriber's NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2060. He cleaned the GPU and checked that the chip was not damaged before replacing the aluminum cooler. After cleaning and scraping off the damaged portion, he used a router to repair the base and the video card resumed normal operation at normal temperatures.
Liquid metal on an aluminum heat sink graphics card causes this