An exclusive AMD partner document unveils anticipated features of the Ryzen 8000 series CPUs, which are expected to offer a substantial speed increase without any radical innovations.
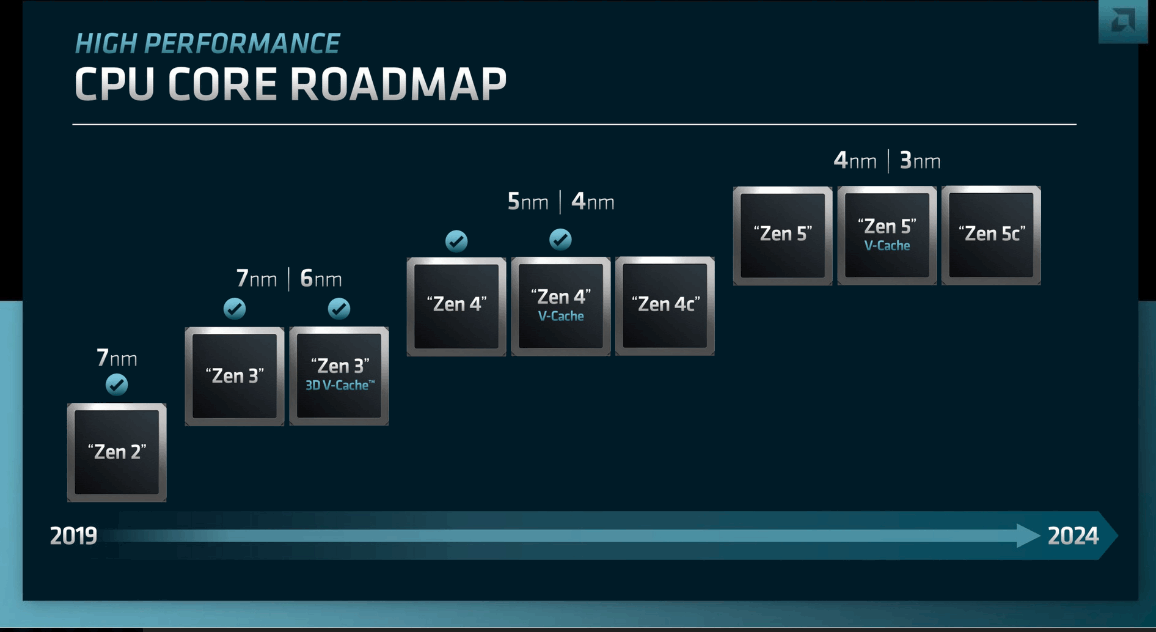
The series is likely to include CPUs with core counts ranging from 6 to 16, thermal design power (TDP) from 65 to 170 watts, and a maximum L3 cache memory of 64 MB. These specifications closely resemble the Ryzen 7000 series, except for the additional cache in the X3D models. A previously published AMD roadmap supports these findings.
Notably, the new Zen 5 architecture is speculated to deliver significant improvements in speed and efficiency compared to previous generations. This is thanks to TSMC's advanced N3E or N3P nodes, which provide up to an 18% performance boost while reducing power consumption by 34%. With similar TDPs, we can expect a noticeable performance improvement and potentially higher clock speeds.
However, these projections remain speculative for now, as the document indicates that the processor series will not be released until the second half of 2024. As previously speculated, the core count based on the Zen 5 architecture and manufactured on TSMC's 4-nanometer process will remain unchanged.
A reliable document available to the author but withheld for source protection reveals key details about the AMD Ryzen 8000, codenamed Granite Ridge, in the desktop segment. The desktop variant of AMD Ryzen 8000 will include the following features: Zen 5 CCDs (Eldora), Zen 5 CPU Cores (Nirvana), 6 to 16 Zen 5 processor cores, 65 to 170 watts TDP, up to 64 MiByte L3 cache and 16 MiByte L2 cache, manufacturing on N3E or N3P nodes at TSMC, and expected release in the second half of 2024.
According to this information, AMD Ryzen 8000, also known as Granite Ridge, will retain the maximum number of processor cores and the size of the fast L3 cache, similar to Ryzen 7000 (Raphael). If all goes according to plan, AMD aims to introduce these desktop processors in the latter half of the year. The transition from N5 to N3 process technology promises a significant improvement in efficiency and performance. TSMC's N3 process is projected to offer 10 to 15 percent higher speed with the same power consumption, or alternatively, 25 to 30 percent lower power consumption with the same speed. Furthermore, the logic density is expected to increase by a factor of 1.6, and N3 chip production has been underway since the second half of 2022.