Article Page 2 - It's all about the Fins
FinFET background
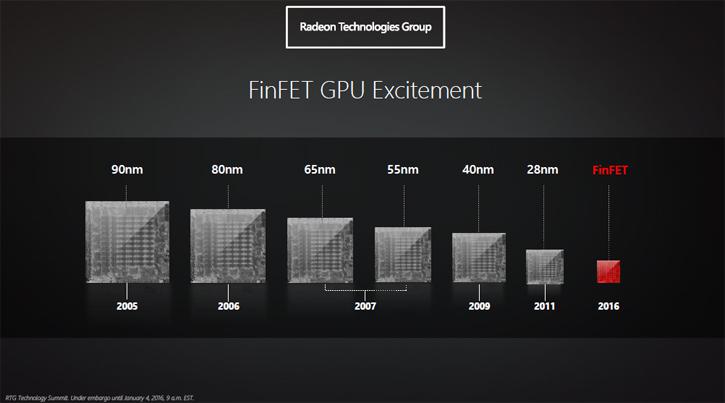
Key to all this energy efficiency and perf per watt related to the smaller fab at 16nm and preferably 14nm is the FinFEt design. I like to call them transistors with wings. To keep things steady and stable without too much leakage, you need fins. FinFET technology has been born as a result of the many levels of complexity based on shrinking micro-processor architectures. We need to do it, we grab Moore's law for a second. Admittedly we have to say, the man was right and his thesis that the number of transistors on a given area of silicon doubles every two years, has been valid for many years. But this also creates bigger problems each time that die shrinks.
If we go back to 1977, the The 6800 was popular in computer peripherals, test equipment applications and point-of-sale terminals. The MC6802, introduced in 1977, included 128 bytes of RAM and an internal clock oscillator on chip. The MC6801 and MC6805 included with RAM, ROM and I/O on a single chip were popular in automotive applications. The 8-bit MC6800 microprocessor, designed and first manufactured by Motorola chip included serial and parallel interface ICs, RAM, ROM and other support chips, it just 5000 transistors.
Next to that the size for the 6800 5.4mm x 5.4mm ... that size sounds familiar right (hint: Fiji with 9 Billion transistors)? Yes, today's micro-processors have many orders of magnitude more, the recent FIJI based Radeon R9 Fury X has 8.9 Billion transistors. There are limits to the scalability of the individual devices and as process technologies continued to shrink towards 20 nm, it became impossible to achieve the proper scaling of various device parameters. Here you are looking at one of the reasons for the failure of the 20nm design, leakage resulting into low yields. It was therefore necessary to look at other more revolutionary options like a change in transistor structure from the traditional planar transistor, behold the FinFET design.
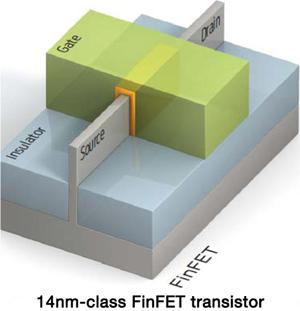
Finfet is a leap in both CPU and GPU advancement if you think in terms of a small form factor design. Considering the number of transistor used have still been doubling each year, you need to shrink transistors. Doubling of transistors equals to double leakage. FinFET is to drive GPUS designs towards a 14 and/or 16nm fabrication. In a FinFET, the FET gate (the green block on the above transistor example) wraps around three sides of the transistor's elevated channel, or "fin." This forms conducting channels on three sides of the vertical fin structure. This solution offers more control over current compared to traditional planar transistors. Multiple fins can be used to provide more current. The gate orientation is at right angles to the vertical fin. And to traverse from one side of the fin to the other it wraps over the fin, enabling it to interface with three side of the fin (or channel).
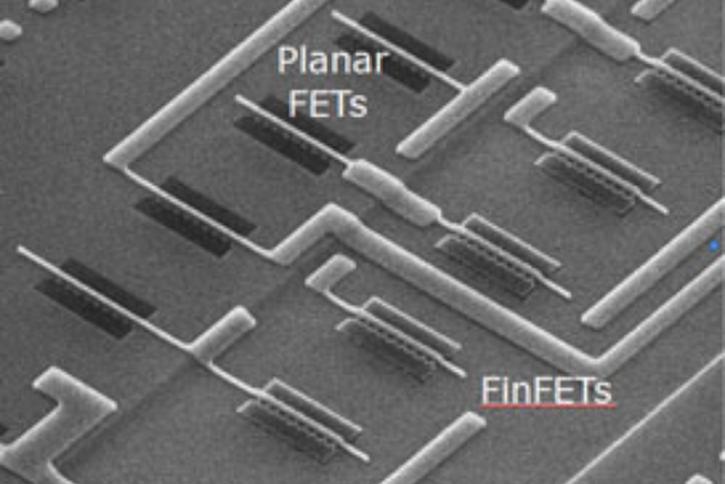
FinFET technology takes its name from the fact that the FET structure used looks like a set of fins when viewed - photo courtesy of imec. And yes 7nm Finfet designs are already work in progress.
So we learned that the main characteristic of the FinFET is that it has a conducting channel wrapped by a thin silicon "fin" from which FinFET gets its name. The thickness of the fin determines the effective channel length of the device. In terms of its structure, it typically has a vertical fin on a substrate which runs between a larger drain and source area. This protrudes vertically above the substrate as a fin.
This form of gate structure provides improved electrical control over the channel conduction and it helps reduce leakage current levels and overcomes some other short-channel effects. FinFET is not an AMD invention, but they use the design. It dates back to 1989 by design, in 2000 UC Berkeley names it FinFET and it was Intel that actually took the FinFET in production in 2012 for their processors. Last words on the topic: summing it up FinFET wraps the gate which increases surface area, this makes the transistors faster and knocks the leakage out. It means a bigger increase in uniformity and a substantial improvement in performance and power over traditional bulk devices. AMD is seeing 20 to 35% more performance with 50 to 60% less power consumption over 28nm. FinFET is all about perf versus power.
DisplayPort 1.3
Noted in our last report as well, now updating. The new 2016 GPUs will all support DisplayPort 1.3 and HDMI 2.0a - DP is a digital display interface developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA). The interface is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such as a computer monitor, though it can also be used to carry audio, USB, and other forms of data as well actually.
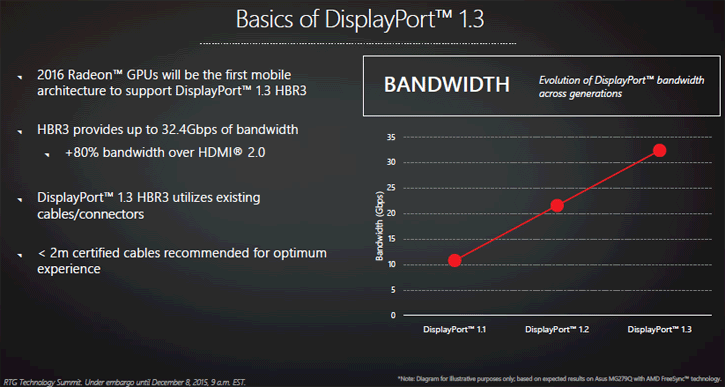
The 2016 upcoming (new) AMD Radeon GPUs will offer Display port 1.3 compatibility which offers an increased overall transmission bandwidth to 32.4 Gbit/s with the new HBR3 mode featuring 8.1 Gbit/s per lane (up from 5.4 Gbit/s with HBR2 in version 1.2), totalling 25.92 Gbit/s with overhead removed. That is over 80% the bandwidth that HDMI 2.0 offers. This enabled enables 4k gaming run on 120 Hz monitors. 4K 120Hz panels will be available in q4 2106. Low framerate compensation will be included in there as well btw. This kind of bandwidth (32.4 Gbit/s) allows for 5K displays (5120×2880 px) in RGB mode, and 8K UHDTV displays at 7680×4320 (16:9, 33.18 megapixels) using 4:2:0 sub-sampling at 60 Hz, all using just one cable.
The bandwidth also allows for two UHD (3840×2160 px) computer monitors at 60 Hz in 24-bit RGB mode using Coordinated Video Timing, a 4K stereo 3D display, or a combination of 4K display and USB 3.0 as allowed by DockPort. The new standard features HDMI 2.0 compatibility mode with HDCP 2.2 content protection. It also supports VESA Display Stream Compression, which uses a "visually loss-less" low-latency algorithm based on predictive DPCM and YCoCg-R color space and allows increased resolutions and color depths and reduced power consumption.
That's it for this update.
H.