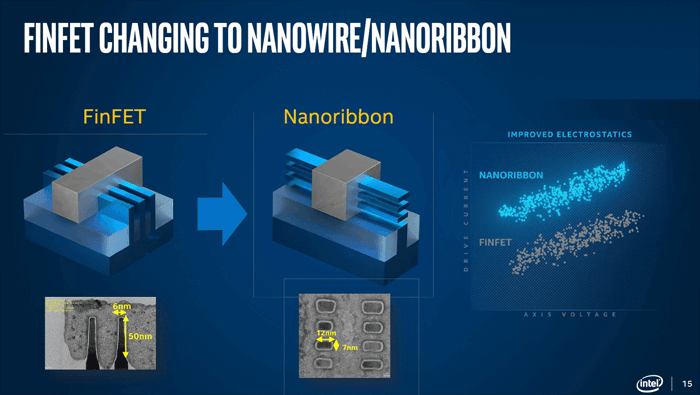
Intel introduces RibbonFET, a new transistor architecture, which it plans to use in its Intel 20A process starting in 2024, according to the manufacturer. Gate-all-around transistor is Intel's implementation.
In addition, Intel will offer chips that can be powered through the back. Current nodes use finfet transistors, which are being replaced by RibbonFETs (ribbon field effect transistors). When Intel's node Intel 20A is introduced in 2024, it will be equipped with the new transistor architecture. Intel calls its '2nm' process. These transistors are smaller and faster to switch, which should lead to better performance, according to Intel's announcement.
A gate-all-around transistor, or RibbonFETis the successor to the finfet, other chip manufacturers are also working on gaa transistors. A 3nm node based on Samsung's gaa transistors is expected to be available by 2022. In 2023, TSMC is expected to deploy gaa transistors at its 2nm node. Nodes up to 3nm will continue to use finfet transistors, the Taiwan-based chip maker said last year. RibbonFET and PowerVia will be combined by Intel. Intel's new powering technology is known as Powering through the backside, there are fewer power leaks while higher clock speeds can be achieved.
By using nano-sized silicon vias to supply power from the back, Intel hopes to eliminate the need for external power supplies. TSVs in current chip designs are up to 500 times smaller, Intel claims. Because the bottom layer can be used for the power supply, and the top layer for the transistors, Intel's PowerVia technology allows wafers to be designed more efficiently and more cost-effectively.
As early as 2024, processors with RibbonFET and PowerVia will be available. Intel has not yet announced which processors it will use the techniques in.
Intel introduces RibbonFET transistor architecture