NVIDIA has announced the release of new tools that make real-time path tracing more accessible to game developers, thus accelerating the creation of ultra-realistic game worlds. The announcement was made at the Game Developers Conference (GDC) 2023
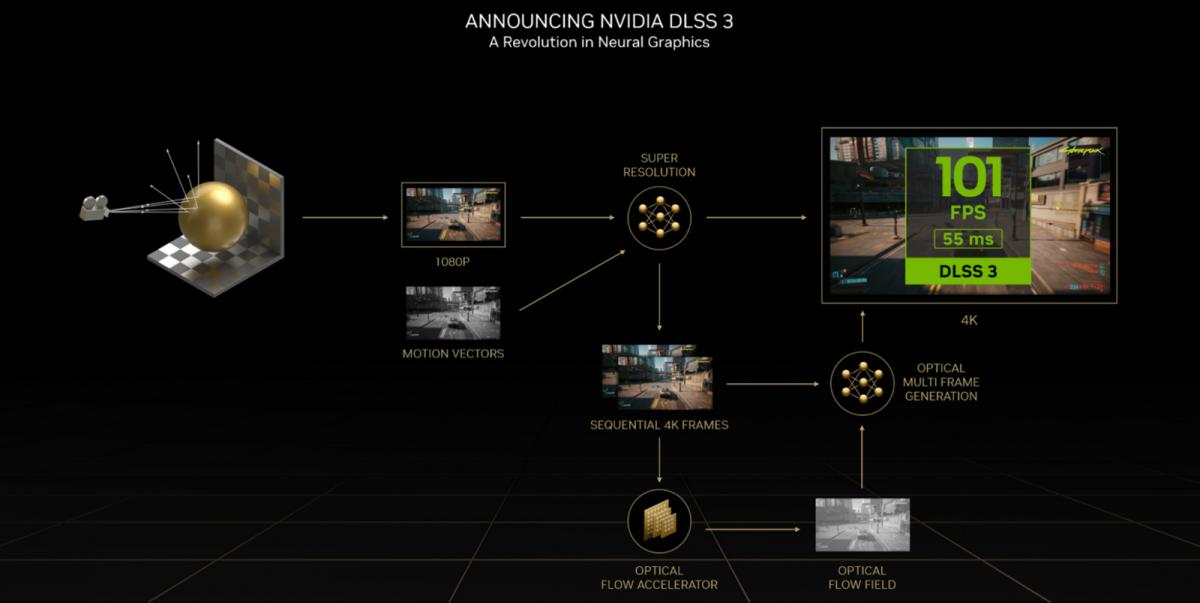
Alongside the launch of the NVIDIA Ada Lovelace architecture, which includes DLSS 3 - a technology that sets new standards for AI in game rendering. One of the major breakthroughs in DLSS 3 is Frame Generation, a new performance multiplier that creates entirely new frames using AI. The technology is powered by NVIDIA GeForce 40 series and the Optical Flow Accelerator, making real-time path tracing possible for the first time.
Since the announcement, 28 top games and applications have adopted DLSS 3, including A Plague Tale Requiem, Portal with RTX, and Cyberpunk 2077, with some games experiencing almost triple the frames-per-second. Developers can now access DLSS Frame Generation through the Streamline 2.0 SDK, an open-source cross-IHV framework that simplifies the integration of features like DLSS 3.
Epic Games also announced that the DLSS Frame Generation plugin will be available in its next release of Unreal Engine, in addition to NVIDIA Reflex low latency technology available through UE5. With these tools, developers can boost game performance while providing a highly responsive experience for players.
Together, NVIDIA and Epic Games are pushing the boundaries of AI in game development, bringing real-time path tracing a step closer to reality. "NVIDIA DLSS 3 introduces truly impressive frame generation technology and the Unreal Engine 5.2 plugin will offer developers a great choice for increased quality and performance of their games," said Nick Penwarden, VP of Engineering at Epic Games.
Integration of real-time path tracing technology simplified
Real-time ray tracing in games was made possible with the introduction of RT cores in the NVIDIA Turing architecture. Since then, NVIDIA has been hard at work on the next challenge.
The RTX Path Tracing SDK accurately re-creates the physics of all light sources in a scene to reproduce what the eye sees in real life. This new SDK gives you the flexibility and customizability to take advantage of proven NVIDIA technologies to suit the following use cases:
- Building a reference path tracer to ensure that your lighting during production is true to life, accelerating the iteration process.
- Building high-quality photo modes for RT-capable GPUs or real-time, ultra-quality modes that take advantage of the Ada Lovelace architecture.
The RTX Path Tracing SDK is the culmination of decades of NVIDIA research. This SDK demonstrates best practices for building a path tracer using the latest versions of the following tools and features:
- DLSS 3 for super-resolution and frame generation, to multiply performance.
- RTX Direct Illumination (RTXDI) for efficient sampling of a high number of shadow casting and dynamic lights.
- NVIDIA Real-Time Denoisers (NRD) for high-performance denoising of all light sources.
- Opacity Micro-Map (OMM) for improving RT performance in scenes with heavy alpha effects.
- Shader execution reordering (SER) for improving shader scheduling, thus increasing performance.
Improving path tracing performance and increasing accessibility
NVIDIA continuously looks for more opportunities to improve the performance of real-time path tracing, which has led to the development of Opacity Micro-Map (OMM), announced at GTC 2022.
At GDC 2023, OMM SDK 1.0 will be available to all developers. OMM allows you to efficiently map complex geometries, such as dense vegetation and foliage, onto triangles and micro-meshes, providing high-level performance in detailed scenes.
To optimize all this new path tracing and AI rendering technology, an update to Nsight Systems is available now. This release brings support for profiling OMM in Vulkan applications, enabling you to intercept malfunctioning OMM functions. An upcoming Nsight Graphics update will give you the ability to inspect and debug OMM’s performance gain.
Caustics
Lastly, NVIDIA is making it easier for all Unreal Engine developers to start their path-tracing journey with a set of new ray-tracing features in the NVIDIA Caustics branch of Unreal Engine 5.
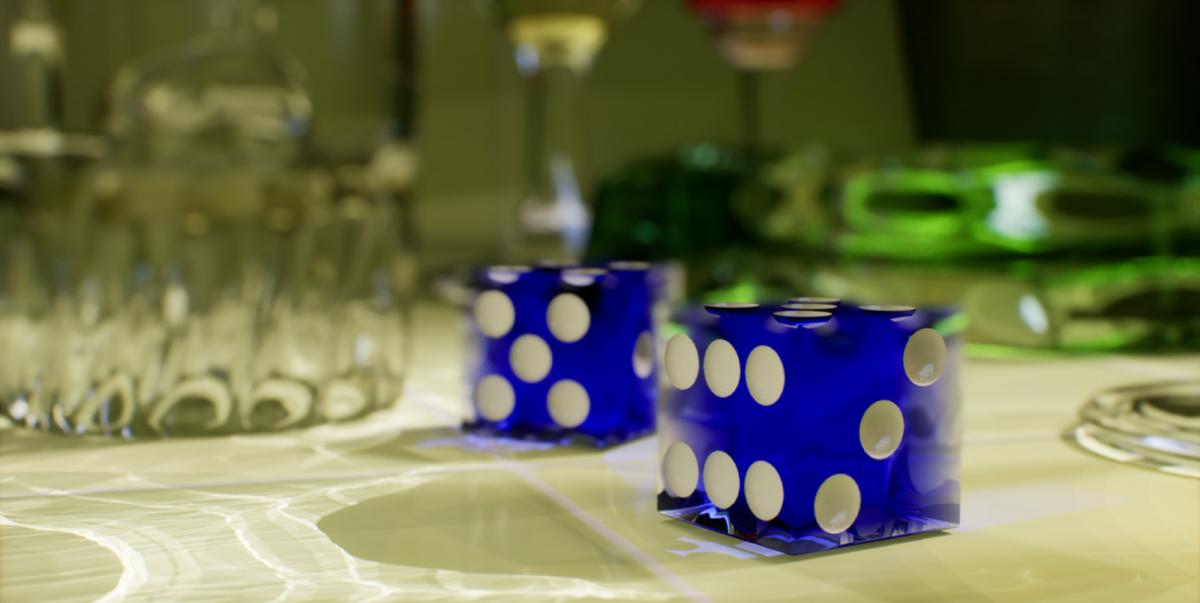
Caustics is an optical phenomenon that exists all around us and is invisible to the naked eye until it hits a reflective material like glass and produces a curved region of light. This technology is available now through the UE 5.1 Caustics branch and makes it easier to leverage caustic effects around metallic and translucent meshes and water surfaces. For more information about how to get access, see Accessing Unreal Engine source code on GitHub. Ray-traced depth of field is a standout feature of this branch. In traditional rasterization workflows, camera depth of field is a challenge to calculate translucent objects accurately. With the Caustics branch, such camera effects are achievable.
Figure (dices) below shows a traditional rasterization pipeline camera depth of field with translucency challenges.
NVIDIA Brings Ultra-Realism to Video Games with AI and Path Tracing Technologies