Specifications & Features
Specifications & Features
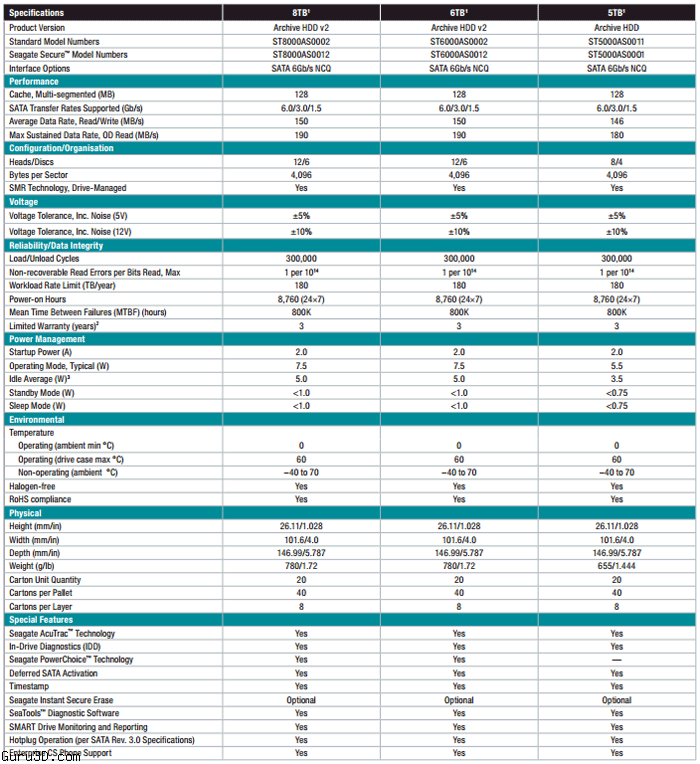
Seagate has several models available in te archive range, including 5T B / 6 TB HDD and 8 TB HDDs. That last one can bu found for under 250 EURO. These drives are intended for NAS storage and obviously are not the fastest platters spinning at 5,900 RPM. However, the new models hold 8 TB of data and that simply means you get to have a lot of TB for your dough.
The Seagate Archive series are based on Shingled magnetic recording (SMR), a magnetic storage data recording technology used in hard disk drives (HDDs) to increase storage density and overall per-drive storage capacity. Conventional hard disk drives record data by writing non-overlapping magnetic tracks parallel to each other (perpendicular recording), while shingled recording writes new tracks that overlap part of the previously written magnetic track, leaving the previous track narrower and allowing for higher track density. Thus, the tracks partially overlap similar to roof shingles. This approach was selected because physical limitations prevent recording magnetic heads from having the same width as reading heads, leaving recording heads wider. The overlapping-tracks architecture may slow down the writing process since writing to one track overwrites adjacent tracks, and requires them to be rewritten as well. Device-managed SMR devices hide this complexity by managing it in the firmware, presenting an interface like any other hard disk, while other SMR devices are host-managed and depend on the operating system to know how to handle the drive, and only write sequentially to certain regions of the drive. Seagate has been shipping device-managed SMR hard drives since September 2013, while referring to an increase in overall hard disk drive capacity of about 25%, compared to non-shingled storage.
The Seagate Archive series HDDs of 8 TB have a SATA 6 Gbps interface. At the website these puppies are listed have an idle power consumption of 5 W with an average operating power of 7.5 W.
- Form factor: 3.5"
- RPM: 5900
- Cache: 128 MB
- Power: 7.5 W (functional), 5 W (idle)
- Warranty 3 years
Standby power consumption of less than 1 W. The specification sheet reveals it's capable of throughput speeds of up to 190 MB/s. The HDDs are listed starting 225~249 EURO.
"Customers today need storage solutions to support a diverse, and sometimes very specialized, set of applications and workload requirements," said Scott Horn, vice president of marketing at Seagate. "In designing our products, we look closely at the type of data being stored, performance needs, power requirements, environmental operating conditions, network topologies, uptime demand and more, to ensure our customers receive the right storage technology for the job. This thoughtful approach has enabled us to deliver the most compelling 8 TB portfolio available in the industry."
Within the cloud and traditional enterprise markets, businesses need high capacity and extremely reliable data storage solutions. Seagate's 8 TB Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD drive addresses these needs by incorporating proven conventional magnetic recording hard drive technology, backed by nine generations of data center innovation. Enterprise customers also want world class performance from their storage solutions and the 8 TB Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD delivers for them with a 100 percent increase in random read/write performance compared to previous generations, driving a vast improvement in IT performance across the enterprise.
Small- and medium-sized businesses require high reliability too, but they also need storage solutions that can scale to support enterprise class performance as business mandates change and the company grows. Seagate's 8 TB Enterprise NAS HDD takes conventional hard drive recording technology to the next level by providing one third more storage density for any tower or rack mount solution compared to the previous 6 TB generation drive. This density advantage translates to fewer drives without sacrificing capacity, reducing power consumption and saving valuable space in servers and data centers to help improve IT cost structures and service value to the organization.