Setup | Noise | Power consumption | Heat levels
Hardware installation
Installation of the product really is easy. Seat the card into the PC (no need to connect a 6-pin power connectors). You can now turn on your PC, boot into Windows, install the latest GeForce driver and after a reboot all should be working. No further configuration is required or needed.
Energy consumption
We'll now show you some tests we have done on overall power consumption of the PC. Looking at it from a performance versus wattage point of view, the power consumption is downright low for a product of this caliber.
The methodology is simple: We have a device constantly monitoring the power draw from the PC. After we have run all our tests and benchmarks we look at the recorded maximum peak; and that's the bulls-eye you need to observe as the power peak is extremely important. Bear in mind that you are not looking at the power consumption of the graphics card, but the consumption of the entire PC.
Our test system is a power hungry Core i7 965 / X58 based and overclocked to 3.75 GHz. Next to that we have energy saving functions disabled for this motherboard and processor (to ensure consistent benchmark results).
Our ASUS motherboard also allows adding power phases for stability, which we enabled as well. I'd say on average we are using roughly 50 to 100 Watts more than a standard PC due to these settings and then add the CPU overclock, water-cooling, additional cold cathode lights etc.
Keep that in mind. Our normal system power consumption is much higher than your average system.
Single GPU GT 240
- System in IDLE = 219 Watts
- System with GPU in FULL Stress = 282 Watts
- Measured difference (100% GPU load) = 63 Watt on hefty GPU utilization
The monitoring device is reporting a maximum system wattage peak at roughly 285, this is simply low and certainly remains within acceptable levels.
Recommended Power Supply
So here's my power supply recommendation:
- The card requires you to have a 400 Watt power supply unit at minimum if you use it in a high-end system. That power supply needs to have (in total accumulated) at least 35 Amps available (accumulated) on ALL +12 volts rails.
There are many good PSUs out there, please do have a look at our many PSU reviews as we have loads of recommended PSUs for you to check out in there. What would happen if your PSU can't cope with the load?:
- bad 3D performance
- crashing games
- spontaneous reset or imminent shutdown of the PC
- freezing during gameplay
- PSU overload can cause it to break down
The core temperature
Let's have a look at the temperatures this huge cooler offers.
We now fire off a hefty shader application at the GPU and start monitoring temperature behavior as it would be when you are gaming intensely and continuously, we literally stress the GPU 100% here.. We measured at a room temperature of 21 degrees Celsius.
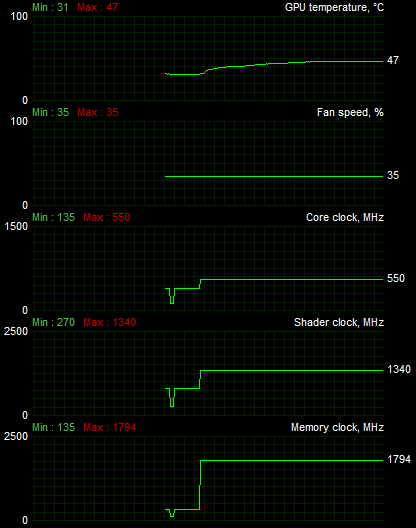
Now we report at two stages the GPU in IDLE and under stress. Here's what we get returned:
| Card setting | TEMP IDLE C | TEMP FULL C |
| MSI GeForce GT 240 | 31 | 47 |
As you can see we get very respectable temperatures returned. When we completely stress out the GPU 100% for a while, temperatures rise towards roughly 70 degrees C (158 F), that's fine.
But is the cooler very loud then?
Noise Levels coming from the graphics card
When graphics cards produce a lot of heat, usually that heat needs to be transported away from the hot core as fast as possible. Often you'll see massive active fan solutions that can indeed get rid of the heat, yet all the fans these days make the PC a noisy son of a gun. I'm doing a little try out today with noise monitoring, so basically the test we do is extremely subjective. We bought a certified dBA meter and will start measuring how many dBA originate from the PC. Why is this subjective you ask? Well, there is always noise in the background, from the streets, from the HD, PSU fan etc etc, so this is by a mile or two not a precise measurement. You could only achieve objective measurement in a sound test chamber.
The human hearing system has different sensitivities at different frequencies. This means that the perception of noise is not at all equal at every frequency. Noise with significant measured levels (in dB) at high or low frequencies will not be as annoying as it would be when its energy is concentrated in the middle frequencies. In other words, the measured noise levels in dB will not reflect the actual human perception of the loudness of the noise. That's why we measure the dBA level. A specific circuit is added to the sound level meter to correct its reading in regard to this concept. This reading is the noise level in dBA. The letter A is added to indicate the correction that was made in the measurement. Frequencies below 1kHz and above 6kHz are attenuated, where as frequencies between 1kHz and 6kHz are amplified by the A weighting.
| TYPICAL SOUND LEVELS | ||
| Jet takeoff (200 feet) | 120 dBA | |
| Construction Site | 110 dBA | Intolerable |
| Shout (5 feet) | 100 dBA | |
| Heavy truck (50 feet) | 90 dBA | Very noisy |
| Urban street | 80 dBA | |
| Automobile interior | 70 dBA | Noisy |
| Normal conversation (3 feet) | 60 dBA | |
| Office, classroom | 50 dBA | Moderate |
| Living room | 40 dBA | |
| Bedroom at night | 30 dBA | Quiet |
| Broadcast studio | 20 dBA | |
| Rustling leaves | 10 dBA | Barely audible |
The noise levels coming from the card are perfectly fine, in idle you will not hear the card as we measured 39 DBa. Which is below the threshold of noise from the PC itself.
Once the GPU starts to heat up the fan RPM will go up. The card however remains steady and we measure roughly 43 dBA which a decent enough noise level. It's alright -- but not silent.
