Voltage dips and acoustic Testing
Stability Testing The PSU
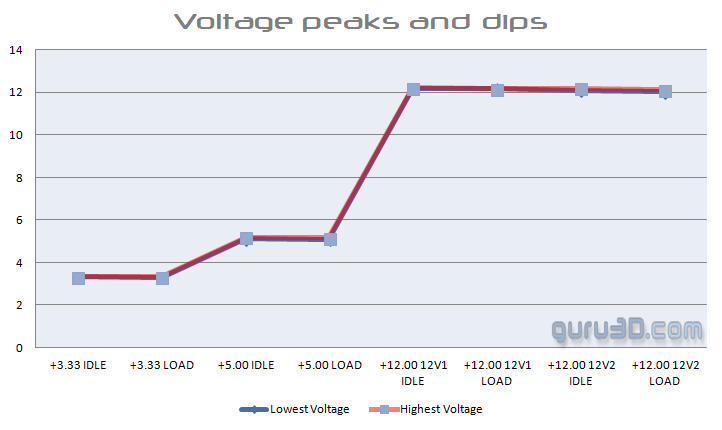
During our tests, we also monitor the voltage fluctuations as shown below in both IDLE and LOAD states of the PC. We write down the lowest and highest values we see within a specific PC state. The difference is the fluctuation. If a PSU is unstable, we'd see a lot of variation, differentiation, and discrepancies, which can result in instability.
This is the good old-fashioned Digital MultiMeter work tapping voltage measurement spots on the mobo as well as the power connectors. Once we've gathered all voltage results, we can place them in an easy to understand chart. Look at the chart, the two lines show both the idle and load state of a specific voltage rail, the dark blue one the lowest voltage dip measured, the red one the highest fluctuation. That's your baseline. The ATX specification requires that the PSU needs to stay within a 5% fluctuation; for example, each +12 Volt rail should remain between 11.4 - 12.6 Volts. All results remain far within specification and tolerance thresholds. As you can see, the PSU, when utilized, stays consistent as you can hardly even see the blue line, meaning that the PSU is functioning within ATX specified limits. We tested single and multi-rails. With two cards in multi-GPU, we've been able to set up and utilize four rails. But whatever we tried, it made no substantial enough difference to visualize (which is a good thing for be quiet!).
Acoustic Sound levels (dBA)
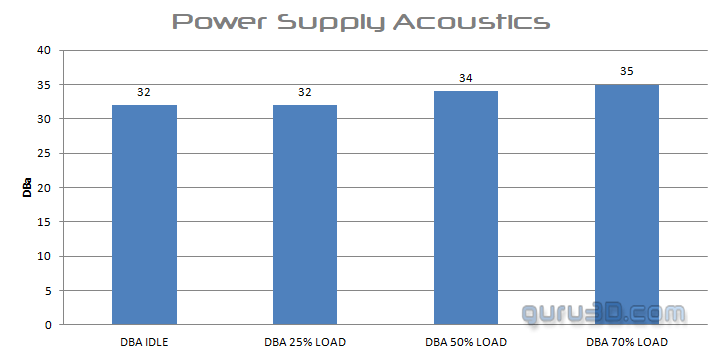
As usual, we grabbed our dBA meter. The human hearing system has different sensitivities at different frequencies. This means that the perception of noise is not at all equal at every frequency. Noise with significant measured levels (in dB) at high or low frequencies will not be as annoying as it would be when its energy is concentrated in the middle frequencies. In other words, the measured noise levels in dB will not reflect the actual human perception of the loudness of the noise. That's why we measure the dBA level. A specific circuit is added to the sound level meter to correct its reading concerning this concept. This reading is the noise level in dBA. The letter A is added to indicate the correction that was made in the measurement.
As always, we measure 75 CM away from the product (usually the distance between you and a desktop computer). This is a subjective test, though.
- At 5~10% load you barely hear the PSU
- At ~ 25% load you barely hear the PSU
- At ~ 50% load you barely hear the PSU
- At ~ 70% load you can mildly hear the PSU