Power Consumption
Power Consumption
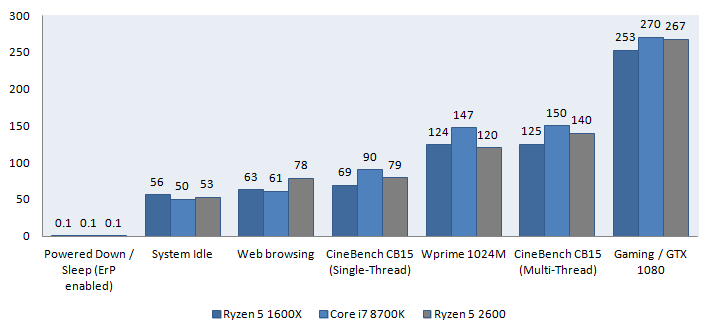
In an IDLE state, a PC (motherboard / processor / GTX 1080 / memory / SSD) consumes roughly 50 Watts. This number depends and will vary per motherboard (added ICs / controllers / wifi / Bluetooth) and PSU (efficiency). Keep in mind that we measure the ENTIRE PC, not just the processor's power consumption. Your average PC can differ from our numbers if you add optical drives, HDDs, soundcards etc.
Various load conditions - there is a dedicated graphics card installed (GTX 1080)
I want to make it very clear that power consumption measurements will differ per PC and setup. Your attached components use power but your motherboard can also have additional ICs installed like an audio controller, 3rd party chips, network controllers, extra SATA controllers, extra USB controllers, and so on. These parts all consume power, so these results are a subjective indication. Next, to that, we stress all CPU cores 100% and thus show peak power consumption. Unless you transcode video with the right software your average power consumption will be much lower. Ryzen 5 2600X and Ryzen 7 2700X definitely consumes more power in heavy-threaded workloads, roughly an additional 35~50 Watts.
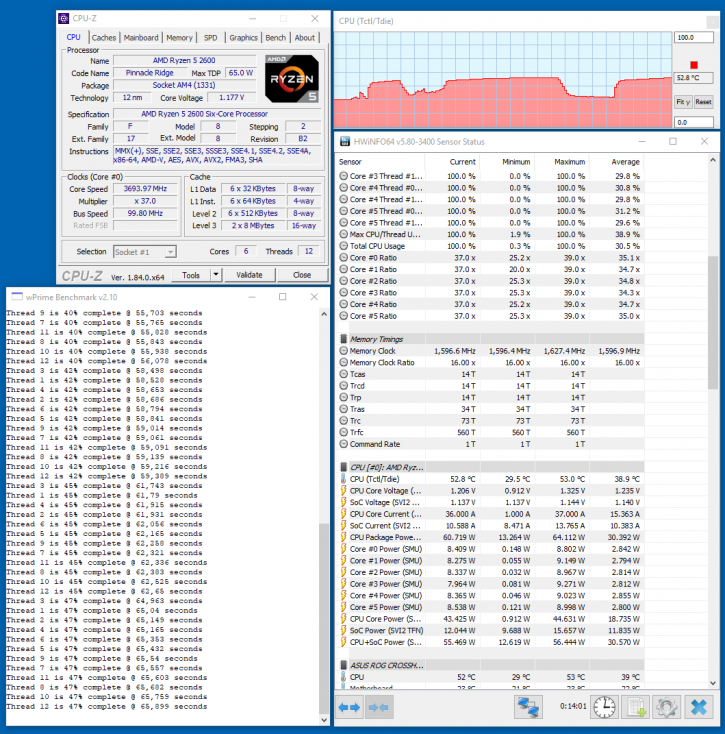
We use a stock Wraith LED (air) cooler in this 2600X review. We reach a max temp of ~55 Degrees C (Tdie). That is running a 1024M Prime test.
Temperature Reporting
To keep a "consistent fan policy," AMD is forcing 10C offset on the Ryzen 2700X but not any of the other Zen+ models. This makes the 2700X report temperature a good 10C above what the sensor reads. The primary temperature reporting sensor of the AMD Ryzen processor is a sensor called “T Control,” or tCTL for short. The tCTL sensor is derived from the junction (Tj) temperature—the interface point between the die and heatspreader—but it may be offset on certain CPU models so that all models on the AM4 Platform have the same maximum tCTL value. This approach ensures that all AMD Ryzen and thus Ryzen Threadripper processors have a consistent fan policy.
| Product Name | True Junction Temp (Tdie) | tCTL Offset for Fan Policy | Temp Reported by (tCTL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Threadripper 1950X | 43°C | 27°C | 70°C |
| Threadripper 1920X | 43°C | 27°C | 70°C |
| Ryzen 7 2700X | 38°C | 10°C | 48°C |
| Ryzen 7 2700 | 38°C | 0°C | 38°C |
| Ryzen 5 2600X | 38°C | 0°C | 38°C |
| Ryzen 5 2600 | 38°C | 0°C | 38°C |
| Ryzen 7 1800X | 38°C | 20°C | 58°C |
| Ryzen 7 1700X | 38°C | 20°C | 58°C |
| Ryzen 7 1700 | 38°C | 0°C | 38°C |
In short, if you use any monitoring software, you need to look at the Tdie as temperature, it's the correct one to look at.