Architectural Details
Up-to 20 MB L2+L3 Cache
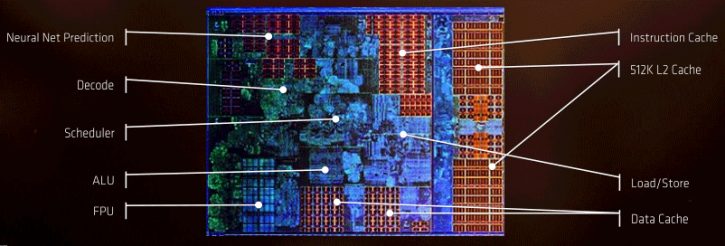
The architecture that is Pinnacle Ridge really is the same as Summit Ridge. So this page looks the same as the version from 2017. The Ryzen caches; all parts are based on the same processor. There is 20 MB (for an 8-core processor) for the L2 and L3 cache, and that matches what we have discussed numerous times.
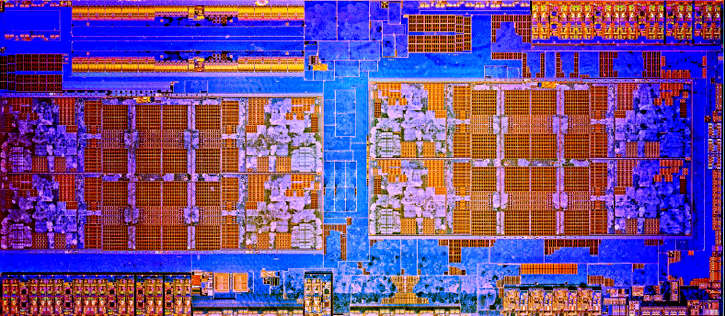
All AMD Ryzen 5 and 7 processors dies holds eight cores
One core out of the eight available
The 8-core part with two four-core CCX units aka Summit and Pinaccle Ridge aka RYZEN, in the end, get a L1 data cache size of 32 KiB, a L1 instruction cache size of 64 KiB and then a L2 cache size of 512 KiB per core.
- L1 8 x 32 Kb Data
- L1 8 x 64 Kb Instruction
- L2 8 x 512 Kbytes
- L3 2 x 8 Mbytes L3
The 6-core part with two four-core CCX units aka Summit Ridge and Pinaccle aka RYZEN, in the end, get a L1 data cache size of 32 KiB, a L1 instruction cache size of 64 KiB and then a L2 cache size of 512 KiB per core.
- L1 6 x 32 Kb Data
- L1 6 x 64 Kb Instruction
- L2 6 x 512 Kbytes
- L3 2 x 8 Mbytes L3
The 4-core part with two four-core CCX units aka Summit Ridge and Pinaccle aka RYZEN, in the end, get a L1 data cache size of 32 KiB, a L1 instruction cache size of 64 KiB and then a L2 cache size of 512 KiB per core.
- L1 4 x 32 Kb Data
- L1 4 x 64 Kb Instruction
- L2 4 x 512 Kbytes
- L3 2 x 8 Mbytes L3
The L3 cache remains an open bigger pool at 8 Mbytes per cluster. Again, one Core Complex Unit holds four processor cores. The processor has dual channel DDR4 support (up-to 3200MHz), AVX2, AES, FMA3, AMD-V SSE 4.1 and 4.2 instruction sets etc. The bus frequency is 100 MHz multiplied by whatever the processor fires off at it. Ryzen is built with a 14nm FinFET fab node, this greatly helps where AMD is with the performance and power consumption. For the transistor aficionados, the number is 4.90 Billion of them.
Technology Highlights
AMD has implemented technology that will make sure that this processor runs applications efficiently and optimized. SenseMI is a set of sensing and adaptive technologies, including an artificial network inside every “Ryzen” processor to anticipate future decisions, preload instructions, and choose the best path through the CPU. AMD is also introducing a new interconnect called AMD Infinity Fabric. This is a new and fast way of connecting various parts within an SoC. Infinity Fabric is not just used in the RYZEN processors, but also in future (Vega) AMD GPUs and (almost) all other AMD chips in the near future. Infinity Fabric allows for faster and better secure connections within a chip. The inter- and intra-chip connector will be standardized and used in many AMD products and, as such, AMD can easily communicate over that very same interconnect. SenseMI technology then; it is based on five parts as shown in the slide below. Pure Power is a technology that allows the Ryzen chips and other Ryzen variants to work as efficiently as possible.
According to AMD, the CPUs are equipped with hundreds of sensors that monitor temperature, voltage and power consumption of all chip segments. Through the Infinity Fabric connections these sensors are all connected to a central control unit, the Infinity System Management Unit. The same network of sensors constantly monitors how much room there is left for extra performance, chip parts can be independently adjusted from each other. Clock frequencies within a split second can be altered in steps of 25 MHz. To understand the euphemism that is SenseMI, everything inside the processor works heterogeneously and optimized. So you get precise boost frequencies matched to power management. What is a simple to grasp manner to understand is that SenseMi will do a lot of analyzing and smart prediction based upon the workload at hand. If I recall correctly, it was back in the summer in a presentation that AMD already announced that the existing Zen branch predictor (the code that predicts the path where branches in code probably will be) was mentioned to have been greatly improved. AMD indicated that has improved thanks to AI-like algorithms and protocols. The new branch predictor has a self-learning system on board, making decisions based on good or bad branches and thus it can adapt and improve on performance based upon specific workloads and surrounding dynamics. Branch prediction is essential for the efficient operation of the processor. Based on applications and workloads it can detect what course or path is better to follow, making the result a faster one. It will analyze the workload and adapt and optimize based on that. The huge gain in RYZEN IPC (now rated at a 52% IPC increase over last –gen) performance is to be found, among other things, right here with much-improved branch prediction.
So decisions are driven by software code execution and anticipate on following decisions, pre-load instructions, choose the best path through the CPU. It’s pretty impressive when you think about it, a processor that optimizes workloads based on algorithms and predictions. AMD will be able to precisely bin and adjust clock frequencies in steps as small as 25 MHz. RYZEN will get that much smarter a prefetcher that anticipates the location of future data accesses by application code. It has a learning algorithm model and learns application data access patterns allowing it to prefetch vital data into local cache memory so it’s ready for immediate use. Efficiency at its best, and after seeing the first results, AMD might have struck gold here.
Back to SenseMI; SenseMI is a monitoring algorithm that monitors and adapts on many levels. On a more arbitrary level this will also mean that SenseMI, with its many sensors, can recognize thermal characteristics and adapt to them, e.g. a better cooler will optimize the processor to go faster and perhaps clock the Turbo bins upwards a notch. Any RYZEN processor with water-cooling will get better temperatures, right? Well, the technology will detect that thermal signature and, as such, it will allow higher boost frequencies with better cooling. Thermal tweaking control at the processor level. And that is where we arrive at XFR/XFR2; XFR alone uses like 100+ sensors (out of a 1000+ sensors per core complex CCX) inside the system and can boost the frequency above the specs available. So it’ll give you a perf boost based on proper cooling and variables like processor binning.