The Embedded GPU - HSA & hUMA
HSA & hUMA
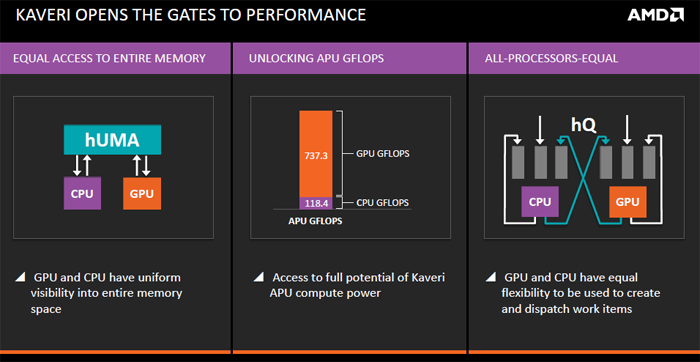
HSA then, the abbreviation you heard so many times already, we'll keep it simple. It's short for Heterogeneous System Architecture and it is what sets Kaveri apart from previous generation APUs. HSA is a way of designing software and hardware to take and distribute computing tasks to both the CPU and GPU, basically taking advantage of the strengths of each serial and parallel processing unit. Graphics processors, for example, excel at performing many calculations simultaneously. So HSA addresses an old problem with existing CPU + GPU architectures by allowing both units to directly access each other's memory pools - a unified memory pool. This eliminates the need for copying in-between buffers which decreases time and work required e.g. better efficiency. Traditionally CPU and GPU have to address different blocks of memory which means data has to be copied between these two blocks. By eliminating the need to copy data between these different blocks, the CPU and GPU can both work on the same data without waiting for it to be copied back and forth. Heterogeneous queueing rebalances how the GPU and CPU interact with each other. While the CPU assigns workloads to the GPU in most current PCs Kaveri's queueing feature allows both processors to dispatch work to each other and create work for themselves. A very nice feature in the Kaveri APUs is the hUMA memory architecture which on its end is a part of the Heterogeneous System Architecture. It allows the APU to make use of a unified memory architecture which would allow cross sharing of system ram between the GPU and CPU.
The GPU In the APU
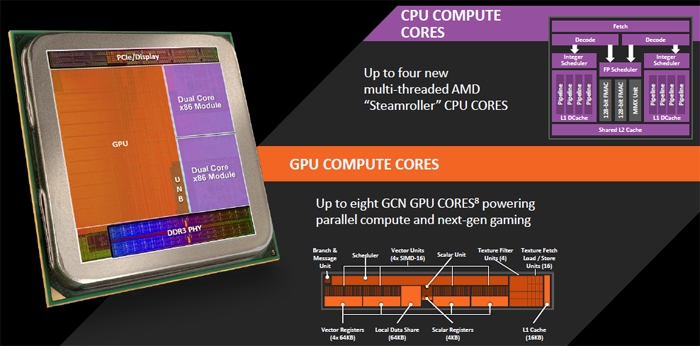
AMD uses the Radeon 7000 series architecture for Kaveri, and as such they have a very strong offering as it is GCN based and in essence the same architecture that you see in say the Series 7000 GPUs (Radeon 7800/7900/260/270/280/290) instead of the previously used VLIW design. Llano APUs made use of AMDs VLIW5 architecture while Trinity and Richland used an updated VLIW4 architecture.
Up to 8 GCN-based GPU cores
- Up to 512 shaders
- Up to 866 MHz
- 8xAA and 16xAF Support
- DirectX 11 /12 support
- Mantle Support
- AMD Eyefinity Technology2 and 4K Ultra HD Support
- DisplayPort 1.2 Support
The APUs make use of the Radeon GCN (Graphics Core Next 2.0) architecture. So next to the four CPU cores, you now will spot 8 GCN based GPU cores as well, up-to eight cores (depending on APU) result into a whopping 512 shader processors (64 cores per GCN Core cluster) and that's where AMD is making the difference opposed to its competition. Basically they compensate with a very powerful graphics engine harbored inside that APU. BTW AMDs claim of "up to 12 compute cores" in its APU line is a little confusing, as it refers to four CPU cores and eight GCN compute units linked via HSA.
| APU | GPU cores | Shader Cores | GPU Clock | DirectX | Video Coding | Mantle | Tdp |
| A10-7870K | 8 | 512 | 866 MHz | 12 | VCE2 | Yes | 95W |
| A10-7850K | 8 | 512 | 720 MHz | 12 | VCE2 | Yes | 95W |
| A10-7700K | 6 | 384 | 720 MHz | 12 | VCE2 | Yes | 95W |
| A8-7650K | 6 | 384 | 720 MHz | 12 | VCE2 | Yes | 65W |
| A8-7600 | 6 | 384 | 720 MHz | 12 | VCE2 | Yes | 65W |
| A8-7600 | 6 | 384 | 720 MHz | 12 | VCE2 | Yes | 45W |
Now the A10-7870K will have 512 shader cores, which resolves to 8 CUs which may boost towards 866 MHz. This roughly equates to say the the Radeon HD 7750 / 7770. The performance is good for an IGP, the shared L2 cache definitely helps out here, but a bottleneck remains graphics memory which is drawn from System Memory, hence for systems with Kaveri APUs faster memory will result into better graphics performance.
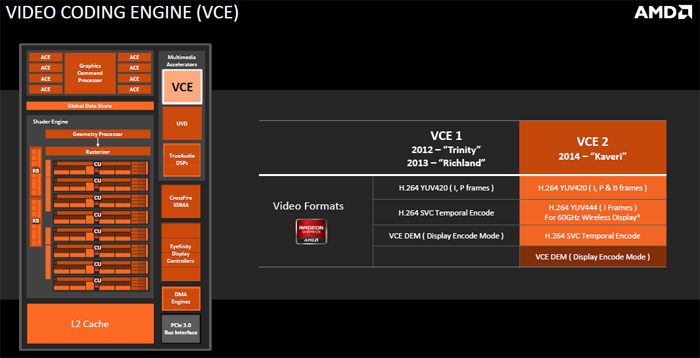
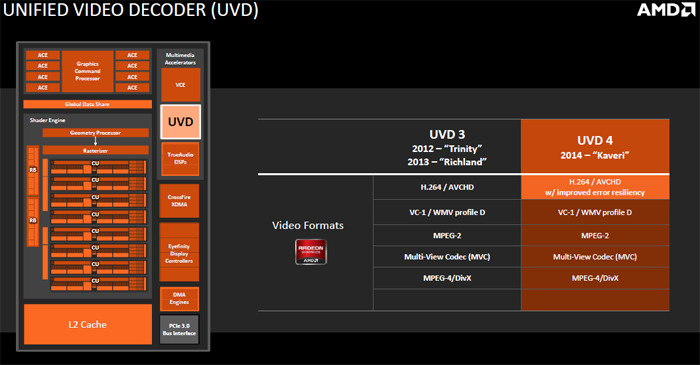
Unified Video Decoder & Video Compression Engine
Kaveri supports hardware decoding of H.264 and VC-1 video codec standards. The chip also has built-in support for video encoding for H.264 via its video compression engine.
- Dedicated hardware to offload video encoding/decoding from CPU
- AMD Picture Perfect support with HD Post-Processing technologies
The AMD Kaveri APUs adds some new high quality video post processing features to improve video. This includes new super- resolution upscaling that can improve how SD quality video looks on HD screens, as well as how 1080P content looks on Ultra HD screens. The IGP will provide support for multiple monitors and all common connectors are supported including HDMI, DVI, DisplayPort and DSUB (VGA).
A new videocodec: h265/hevc
The APU will support h265/hevc as well. The new video codec is up and coming thanks to the rapid adoption of Ultra HD and thus the sheer need to preserve costly bandwidth. Initially we heard that this will be software support rendered over the shader engine ony. High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) is a video compression format and will be a successor to H.264/MPEG-4 AVC (Advanced Video Coding). HEVC is to double the data compression ratio compared to H.264/MPEG-4 AVC at the same level of video quality. It can alternatively be used to provide substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It can support 8K UHD and resolutions up to 8192x4320.